Restriction Endonucleases Products
Cut Smarter with Restriction Enzymes from NEB
With over 45 years of offering restriction enzymes to the research community, NEB has earned the reputation of being a leader in enzyme technologies. Working continuously to be worthy of that distinction, NEB strives to develop enzymes of the highest purity and unparalleled performance.
Convenience
- A vial of 6X Purple Load Dye is included with most restriction enzymes.
- Over 210 restriction enzymes are 100% active in a single buffer – rCutSmart™ Buffer.
- >180 restriction enzymes are Time-Saver qualified, meaning you can digest DNA in 5-15 minutes, or digest DNA safely overnight.
- Choose from >265 restriction enzymes, the largest selection commercially available.
Performance
- Choose a High-Fidelity (HF®) restriction enzyme, which has been engineered for reduced star activity, rapid digestion (5-15 minutes) and 100% activity in rCutSmart Buffer. A vial of 6X Purple Load Dye is included with every HF restriction enzyme.
- All of our restriction enzymes undergo stringent quality control testing, ensuring the highest levels of purity and lot-to-lot consistency.
Use Enzyme Finder to select restriction enzymes by name, sequence, overhang or type.
Choose Product:
- Restriction Endonucleases
- Restriction Endonucleases: A Products
- Restriction Endonucleases: B Products
- Restriction Endonucleases: C-G Products
- Restriction Endonucleases: H-M Products
- Restriction Endonucleases: N-O Products
- Restriction Endonucleases: P-R Products
- Restriction Endonucleases: S Products
- Restriction Endonucleases: T-Z Products
- HF®, Nicking, Master Mix, Time-Saver & Other Products
- Restriction Endonuclease Buffers & Diluents Products
WarmStart® Nt.BstNBI
Restriction Endonucleases: A Products
AatII
Acc65I
AccI
AciI
AclI
AcuI
AfeI
AflII
AflIII
AgeI-HF®
AhdI
AleI-v2
AluI
AlwI
AlwNI
ApaI
ApaLI
ApeKI
ApoI-HF®
AscI
AseI
AsiSI
AvaI
AvaII
AvrII
Restriction Endonucleases: B Products
BaeGI
BaeI
BamHI
BamHI-HF®
BanI
BanII
BbsI
BbsI-HF®
BbvCI
BbvI
BccI
BceAI
BcgI
BciVI
BclI
BclI-HF
BcoDI
BfaI
BfuAI
BglI
BglII
BlpI
BmgBI
BmrI
BmtI-HF®
BpmI
Bpu10I
BpuEI
BsaAI
BsaBI
BsaHI
BsaI-HF®v2
BsaJI
BsaWI
BsaXI
BseRI
BseYI
BsgI
BsiEI
BsiHKAI
BsiWI
BsiWI-HF®
BslI
BsmAI
BsmBI-v2
BsmFI
BsmI
BsoBI
Bsp1286I
BspCNI
BspDI
BspEI
BspHI
BspMI
BspQI
BsrBI
BsrDI
BsrFI-v2
BsrGI-HF®
BsrI
BssHII
BssSI-v2
BstAPI
BstBI
BstEII-HF®
BstNI
BstUI
BstXI
BstYI
BstZ17I-HF®
Bsu36I
BtgI
BtgZI
BtsCI
BtsIMutI
BtsI-v2
Restriction Endonucleases: C-G Products
Cac8I
ClaI
CspCI
CviKI-1
CviQI
DdeI
DpnI
DpnII
DraI
DraIII-HF®
DrdI
EaeI
EagI-HF®
EarI
EciI
Eco53kI
EcoNI
EcoO109I
EcoP15I
EcoRI
EcoRI-HF®
EcoRV
EcoRV-HF®
Esp3I
FatI
FauI
Fnu4HI
FokI
FseI
FspI
Restriction Endonucleases: H-M Products
HaeII
HaeIII
HgaI
HhaI
HincII
HindIII
HindIII-HF®
HinfI
HinP1I
HpaI
HpaII
HphI
Hpy166II
Hpy188I
Hpy188III
Hpy99I
HpyAV
HpyCH4III
HpyCH4IV
HpyCH4V
I-CeuI
I-SceI
KasI
KpnI-HF®
MboI
MboII
MfeI-HF®
MluCI
MluI-HF®
MlyI
MmeI
MnlI
MscI
MseI
MslI
MspA1I
MspI
MspJI
MwoI
Restriction Endonucleases: N-O Products
NaeI
NarI
Nb.BbvCI
Nb.BsmI
Nb.BsrDI
Nb.BssSI
Nb.BtsI
NciI
NcoI
NcoI-HF®
NdeI
NgoMIV
NheI-HF®
NlaIII
NlaIV
NmeAIII
NotI
NotI-HF®
NruI-HF®
NsiI
NsiI-HF®
NspI
Nt.AlwI
Nt.BbvCI
Nt.BsmAI
Nt.BspQI
Nt.BstNBI
Nt.CviPII
WarmStart® Nt.BstNBI
Restriction Endonucleases: P-R Products
PacI
PaeR7I
PaqCI®
PciI
PflFI
PflMI
PI-PspI
PI-SceI
PleI
PluTI
PmeI
PmlI
PpuMI
PshAI
PsiI-v2
PspGI
PspOMI
PspXI
PstI
PstI-HF®
PvuI-HF®
PvuII
PvuII-HF®
RsaI
RsrII
Restriction Endonucleases: S Products
SacI-HF®
SacII
SalI
SalI-HF®
SapI
Sau3AI
Sau96I
SbfI-HF®
ScaI-HF®
ScrFI
SexAI
SfaNI
SfcI
SfiI
SfoI
SgrAI
SmaI
SmlI
SnaBI
SpeI-HF®
SphI
SphI-HF®
SrfI
SspI-HF®
StuI
StyD4I
StyI-HF®
SwaI
Restriction Endonucleases: T-Z Products
TaqI-v2
TfiI
TseI
Tsp45I
TspMI
TspRI
Tth111I
XbaI
XcmI
XhoI
XmaI
XmnI
ZraI
HF®, Nicking, Master Mix, Time-Saver & Other Products
AatII
Acc65I
AccI
AciI
AclI
AcuI
AflII
AgeI-HF®
AhdI
AluI
AlwNI
ApaI
ApaLI
ApeKI
ApoI-HF®
AscI
AseI
AvaI
AvaII
AvrII
BaeGI
BaeI
BamHI
BamHI-HF®
BbsI
BbsI-HF®
BbvI
BciVI
BclI
BclI-HF
BcoDI
BfuAI
BglI
BglII
BlpI
BmgBI
BmtI-HF®
BpmI
BpuEI
BsaAI
BsaHI
BsaI-HF®v2
BsaWI
BsaXI
BseRI
BsgI
BsiEI
BsiWI
BsiWI-HF®
BslI
BsmAI
BsmBI-v2
BsmI
BsoBI
Bsp1286I
BspCNI
BspEI
BspHI
BspQI
BsrBI
BsrDI
BsrGI-HF®
BsrI
BssHII
BstBI
BstEII-HF®
BstNI
BstUI
BstXI
BstYI
BstZ17I-HF®
Bsu36I
BtgI
BtsCI
Cac8I
ClaI
CspCI
CviQI
DdeI
DpnI
DpnII
DraI
DraIII-HF®
DrdI
EagI-HF®
EarI
Eco53kI
EcoNI
EcoO109I
EcoP15I
EcoRI
EcoRI-HF®
EcoRV
EcoRV-HF®
Esp3I
Fnu4HI
FseI
FspI
HaeIII
HhaI
HincII
HindIII-HF®
HinfI
HinP1I
HpaII
HphI
Hpy166II
HpyAV
HpyCH4IV
HpyCH4V
I-CeuI
I-SceI
KpnI-HF®
MboI
MfeI-HF®
MluCI
MluI-HF®
MlyI
MmeI
MnlI
MseI
MslI
MspA1I
MspI
MspJI
MwoI
Nb.BbvCI
Nb.BsmI
Nb.BsrDI
Nb.BssSI
Nb.BtsI
NciI
NcoI
NcoI-HF®
NdeI
NgoMIV
NheI-HF®
NlaIII
NotI
NotI-HF®
NruI-HF®
NsiI
NsiI-HF®
NspI
Nt.AlwI
Nt.BbvCI
Nt.BsmAI
Nt.BspQI
Nt.BstNBI
Nt.CviPII
PacI
PaeR7I
PflFI
PflMI
PI-PspI
PI-SceI
PmeI
PmlI
PpuMI
PshAI
PstI
PstI-HF®
PvuI-HF®
PvuII
PvuII-HF®
RsaI
SacI-HF®
SacII
SalI
SalI-HF®
SapI
SbfI-HF®
ScaI-HF®
SfiI
SfoI
SmaI
SpeI-HF®
SphI-HF®
SspI-HF®
StuI
StyD4I
StyI-HF®
SwaI
TaqI-v2
TfiI
TseI
TspMI
TspRI
Tth111I
WarmStart® Nt.BstNBI
XbaI
XhoI
XmaI
XmnI
Restriction Endonuclease Buffers & Diluents Products
Diluent A (with rAlbumin)
Diluent B (with rAlbumin)
Diluent C (with rAlbumin)
NEBuffer™ 1
NEBuffer™ 2
NEBuffer™ 3
NEBuffer™ 4
NEBuffer™ r2.1
NEBuffer™ r3.1
NEBuffer™ Set (EcoRI/SspI, DpnII)
NEBuffer™ Set (r1.1, r2.1, r3.1 and rCutSmart™)
rCutSmart™ Buffer
Recombinant Albumin, Molecular Biology Grade
S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)
AatII
Acc65I
AccI
AciI
AclI
AcuI
AfeI
AflII
AflIII
AgeI-HF®
AhdI
AleI-v2
AluI
AlwI
AlwNI
ApaI
ApaLI
ApeKI
ApoI-HF®
AscI
AseI
AsiSI
AvaI
AvaII
AvrII
BaeGI
BaeI
BamHI
BamHI-HF®
BanI
BanII
BbsI
BbsI-HF®
BbvCI
BbvI
BccI
BceAI
BcgI
BciVI
BclI
BclI-HF
BcoDI
BfaI
BfuAI
BglI
BglII
BlpI
BmgBI
BmrI
BmtI-HF®
BpmI
Bpu10I
BpuEI
BsaAI
BsaBI
BsaHI
BsaI-HF®v2
BsaJI
BsaWI
BsaXI
BseRI
BseYI
BsgI
BsiEI
BsiHKAI
BsiWI
BsiWI-HF®
BslI
BsmAI
BsmBI-v2
BsmFI
BsmI
BsoBI
Bsp1286I
BspCNI
BspDI
BspEI
BspHI
BspMI
BspQI
BsrBI
BsrDI
BsrFI-v2
BsrGI-HF®
BsrI
BssHII
BssSI-v2
BstAPI
BstBI
BstEII-HF®
BstNI
BstUI
BstXI
BstYI
BstZ17I-HF®
Bsu36I
BtgI
BtgZI
BtsCI
BtsIMutI
BtsI-v2
Cac8I
ClaI
CspCI
CviKI-1
CviQI
DdeI
DpnI
DpnII
DraI
DraIII-HF®
DrdI
EaeI
EagI-HF®
EarI
EciI
Eco53kI
EcoNI
EcoO109I
EcoP15I
EcoRI
EcoRI-HF®
EcoRV
EcoRV-HF®
Esp3I
FatI
FauI
Fnu4HI
FokI
FseI
FspI
HaeII
HaeIII
HgaI
HhaI
HincII
HindIII
HindIII-HF®
HinfI
HinP1I
HpaI
HpaII
HphI
Hpy166II
Hpy188I
Hpy188III
Hpy99I
HpyAV
HpyCH4III
HpyCH4IV
HpyCH4V
I-CeuI
I-SceI
KasI
KpnI-HF®
MboI
MboII
MfeI-HF®
MluCI
MluI-HF®
MlyI
MmeI
MnlI
MscI
MseI
MslI
MspA1I
MspI
MspJI
MwoI
NaeI
NarI
Nb.BbvCI
Nb.BsmI
Nb.BsrDI
Nb.BssSI
Nb.BtsI
NciI
NcoI
NcoI-HF®
NdeI
NgoMIV
NheI-HF®
NlaIII
NlaIV
NmeAIII
NotI
NotI-HF®
NruI-HF®
NsiI
NsiI-HF®
NspI
Nt.AlwI
Nt.BbvCI
Nt.BsmAI
Nt.BspQI
Nt.BstNBI
Nt.CviPII
WarmStart® Nt.BstNBI
PacI
PaeR7I
PaqCI®
PciI
PflFI
PflMI
PI-PspI
PI-SceI
PleI
PluTI
PmeI
PmlI
PpuMI
PshAI
PsiI-v2
PspGI
PspOMI
PspXI
PstI
PstI-HF®
PvuI-HF®
PvuII
PvuII-HF®
RsaI
RsrII
SacI-HF®
SacII
SalI
SalI-HF®
SapI
Sau3AI
Sau96I
SbfI-HF®
ScaI-HF®
ScrFI
SexAI
SfaNI
SfcI
SfiI
SfoI
SgrAI
SmaI
SmlI
SnaBI
SpeI-HF®
SphI
SphI-HF®
SrfI
SspI-HF®
StuI
StyD4I
StyI-HF®
SwaI
TaqI-v2
TfiI
TseI
Tsp45I
TspMI
TspRI
Tth111I
XbaI
XcmI
XhoI
XmaI
XmnI
ZraI
High-Fidelity (HF®) Restriction Endonucleases
AgeI-HF®
ApoI-HF®
BamHI-HF®
BbsI-HF®
BclI-HF
BmtI-HF®
BsaI-HF®v2
BsiWI-HF®
BsrGI-HF®
BstEII-HF®
BstZ17I-HF®
DraIII-HF®
EagI-HF®
EcoRI-HF®
EcoRV-HF®
HindIII-HF®
KpnI-HF®
MfeI-HF®
MluI-HF®
NcoI-HF®
NheI-HF®
NotI-HF®
NruI-HF®
NsiI-HF®
PstI-HF®
PvuI-HF®
PvuII-HF®
SacI-HF®
SalI-HF®
SbfI-HF®
ScaI-HF®
SpeI-HF®
SphI-HF®
SspI-HF®
StyI-HF®
Homing Endonucleases
I-CeuI
I-SceI
PI-PspI
PI-SceI
Nicking Endonucleases
Nb.BbvCI
Nb.BsmI
Nb.BsrDI
Nb.BssSI
Nb.BtsI
Nt.AlwI
Nt.BbvCI
Nt.BsmAI
Nt.BspQI
Nt.BstNBI
Nt.CviPII
WarmStart® Nt.BstNBI
Restriction Enzymes for Epigenetic Analysis
DpnI
DpnII
HpaII
MspI
MspJI
Time-Saver™ Qualified Restriction Enzymes
AatII
Acc65I
AccI
AciI
AclI
AcuI
AflII
AgeI-HF®
AhdI
AluI
AlwNI
ApaI
ApaLI
ApeKI
ApoI-HF®
AscI
AseI
AvaI
AvaII
AvrII
BaeGI
BaeI
BamHI
BamHI-HF®
BbsI
BbsI-HF®
BbvI
BciVI
BclI
BclI-HF
BcoDI
BfuAI
BglI
BglII
BlpI
BmgBI
BmtI-HF®
BpmI
BpuEI
BsaAI
BsaHI
BsaI-HF®v2
BsaWI
BsaXI
BseRI
BsgI
BsiEI
BsiWI
BsiWI-HF®
BslI
BsmAI
BsmBI-v2
BsmI
BsoBI
Bsp1286I
BspCNI
BspEI
BspHI
BspQI
BsrBI
BsrDI
BsrI
BssHII
BstBI
BstEII-HF®
BstNI
BstUI
BstXI
BstYI
BstZ17I-HF®
Bsu36I
BtgI
BtsCI
Cac8I
ClaI
CspCI
CviQI
DdeI
DpnI
DpnII
DraI
DraIII-HF®
DrdI
EagI-HF®
EarI
Eco53kI
EcoNI
EcoO109I
EcoP15I
EcoRI
EcoRI-HF®
EcoRV
EcoRV-HF®
Esp3I
Fnu4HI
FseI
FspI
HaeIII
HhaI
HincII
HindIII-HF®
HinfI
HinP1I
HpaII
HphI
Hpy166II
HpyAV
HpyCH4IV
HpyCH4V
KpnI-HF®
MboI
MfeI-HF®
MluCI
MlyI
MmeI
MnlI
MseI
MslI
MspA1I
MspI
MwoI
NciI
NcoI
NcoI-HF®
NdeI
NgoMIV
NheI-HF®
NlaIII
NotI
NotI-HF®
NsiI
NspI
PacI
PaeR7I
PflFI
PflMI
PmeI
PmlI
PpuMI
PshAI
PstI
PstI-HF®
PvuI-HF®
PvuII
PvuII-HF®
RsaI
SacI-HF®
SacII
SalI
SalI-HF®
SapI
SbfI-HF®
ScaI-HF®
SfiI
SfoI
SmaI
SpeI-HF®
SphI-HF®
SspI-HF®
StuI
StyD4I
StyI-HF®
SwaI
TaqI-v2
TfiI
TseI
TspMI
TspRI
Tth111I
XbaI
XhoI
XmaI
XmnI
Diluent A (with rAlbumin)
Diluent B (with rAlbumin)
Diluent C (with rAlbumin)
NEBuffer™ 1
NEBuffer™ 2
NEBuffer™ 3
NEBuffer™ 4
NEBuffer™ r2.1
NEBuffer™ r3.1
NEBuffer™ Set (EcoRI/SspI, DpnII)
NEBuffer™ Set (r1.1, r2.1, r3.1 and rCutSmart™)
rCutSmart™ Buffer
Recombinant Albumin, Molecular Biology Grade
S-adenosylmethionine (SAM)
Videos
-
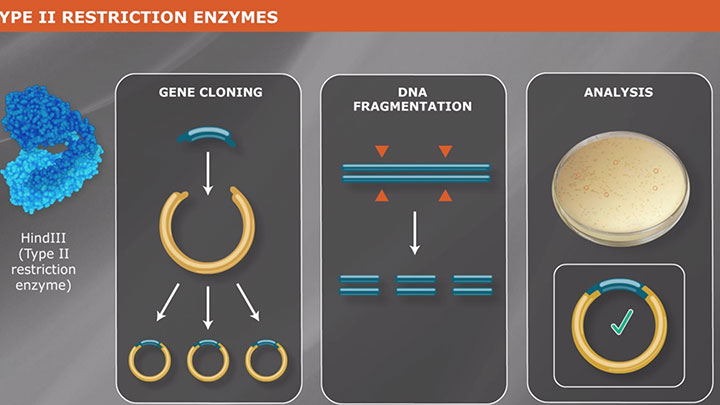
What is a Type II Restriction Enzyme?
Type II restriction enzymes are most commonly used for molecular biology applications, as they recognize stereotypical sequences and produce a predictable cleavage pattern. Learn more about how Type II REs work.
-
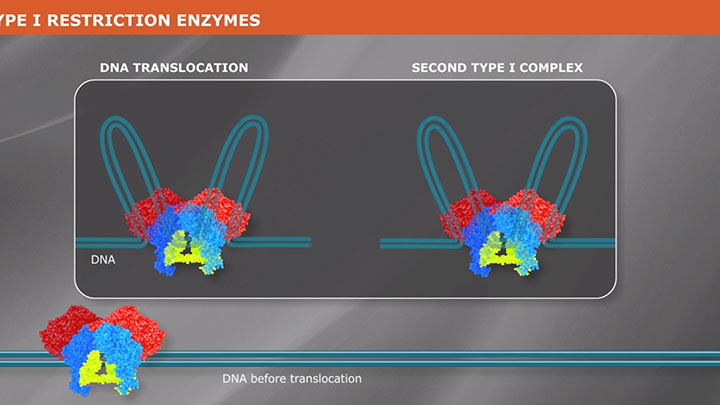
What is a Type I Restriction Enzyme?
Type I restriction enzymes are a group of endonucleases that recognize a bipartite sequence, but do not produce a predictable cleavage pattern. Learn more about how Type I REs work.
-
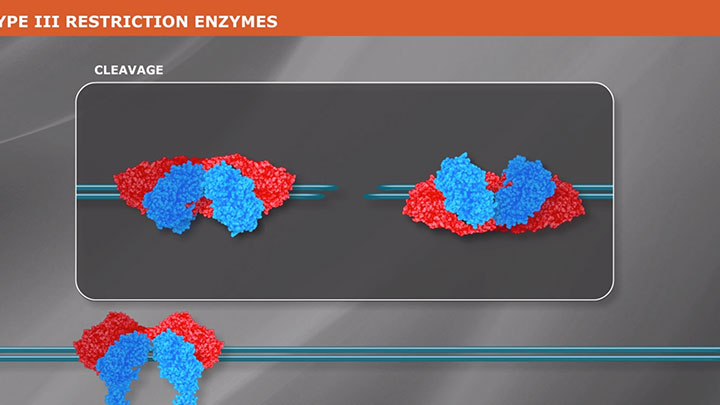
What is a Type III Restriction Enzyme?
Type III restriction enzymes are a group of endonucleases that recognize a non-pallindromic sequence, comprising two inversely oriented sites. Learn more about these poorly understood enzymes.
-

TIME-SAVER™ Qualified Restriction Enzymes
How will Time-Saver™ qualified enzymes save you time? Find out from an NEB scientist.
-
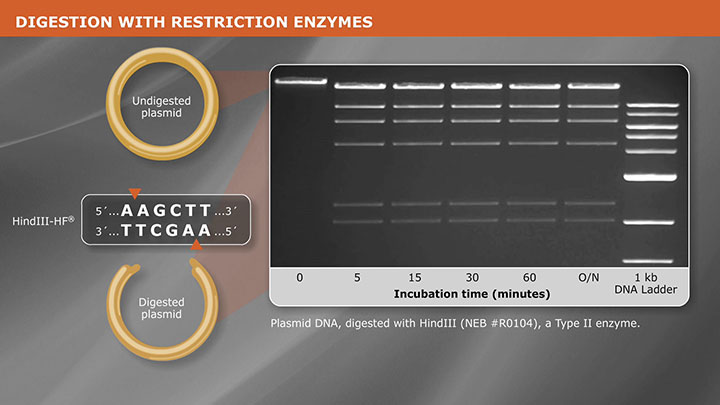
Cloning With Restriction Enzymes
Restriction enzymes are an integral part of the cloning workflow, for generating compatible ends on fragments and vectors. This animation discusses three guidelines for determining which restriction enzymes to use in your cloning experiment.
-

Reduce Star Activity with High-Fidelity Restriction Enzymes
NEB has engineered HF® enzymes to eliminate star activity. Learn how, and what this means for your digests.
-

Standard Protocol for Restriction Enzyme Digests
Let one of NEB's restriction enzyme experts help you improve your technique and avoid common mistakes in digest setup.
-
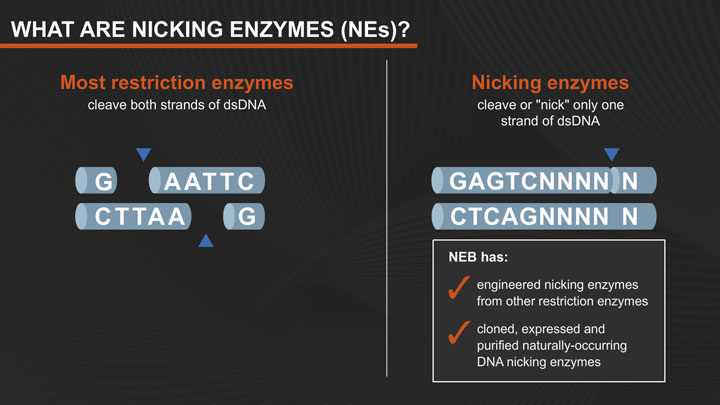
What are Nicking Enzymes and How are They Used?
Learn more about nicking endonucleases (aka nicking enzymes), how they work and their role in different applications including virus detection and SDA.
-

What are Restriction Enzymes?
Watch as Geoff Wilson, Emeritus Scientist, describes what restriction enzymes are and how they revolutionized molecular biology.
-
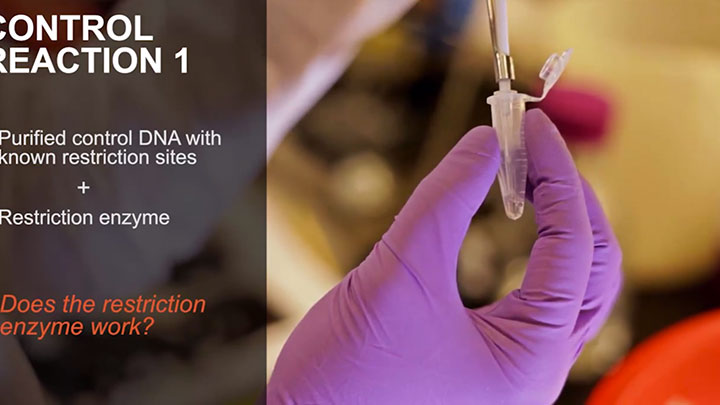
Why is My Restriction Enzyme Not Cutting DNA?
Not getting the cleavage you expected? Let an NEB scientist help you troubleshoot your reaction.
-

Restriction Enzyme Digest Problem: Too Many DNA Bands
Are you finding unexpected bands in your digestion reaction? Here are some tips to help you determine the cause.
-

Restriction Enzyme Digest Protocol: Cutting Close to DNA End
When cutting close to the end of a DNA molecule, make sure you know how many bases to add to the ends of your PCR primers.
-
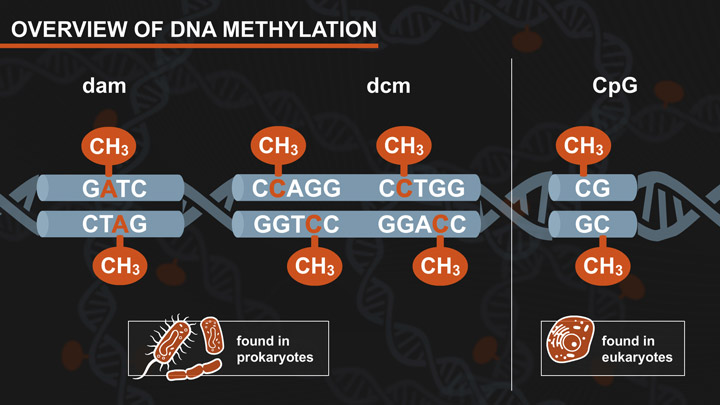
The Effect of DNA Methylation on Restriction Digests
This tutorial explains the effect of DNA methylation on restriction enzyme digestion; including dam, dcm and CpG methylation.
-

Restriction Enzymes in Isothermal Amplification
Isothermal amplification generates many copies of a target sequence in a short period of time, at a constant temperature. Learn more about isothermal amplification.
Ineligible item added to cart
Based on your Freezer Program type, you are trying to add a product to your cart that is either not allowed or not allowed with the existing contents of your cart. Please review and update your order accordingly If you have any questions, please contact Customer Service at freezers@neb.com or 1-800-632-5227 x 8.



