DNA Assembly and Cloning
Which Assembly Method Should I Choose?
To help select the best DNA assembly method for your needs, please use the Product Summary Chart below and our Synthetic Biology/DNA Assembly Selection Chart for more details. If you are new to molecular cloning, you can review the advantages and disadvantages of each method by visiting the Which Molecular Cloning Technique Is Best For You page.

|

|
|
|
NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly |
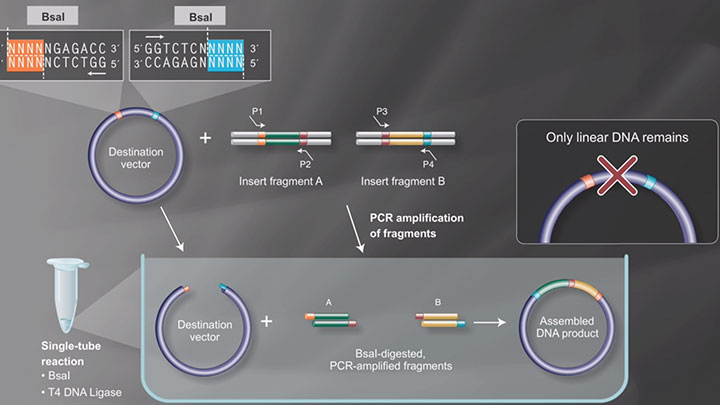
NEBridge® Golden Gate Assembly |
|
|
STEPS IN PROTOCOL |
Single tube (one-pot), only one reaction step |
Single tube (one-pot), only one reaction step |
|
CLONING EFFICIENCY |
>95% |
>95% |
|
FRAGMENT SIZE |
<100 bp to >10kb(1) |
<50 bp to >10 kb(2) |
|
REACTION TIME(S) |
From 15 minutes |
From 5 minutes |
|
FRAGMENT NUMBER |
Up to 12 |
Up to 50+(3) |
|
FORMATS |
Available as Master Mix or full kit with chemically competent cells |
Available as Master Mix or kits with optimized destination plasmid |
|
IDEAL APPLICATION |
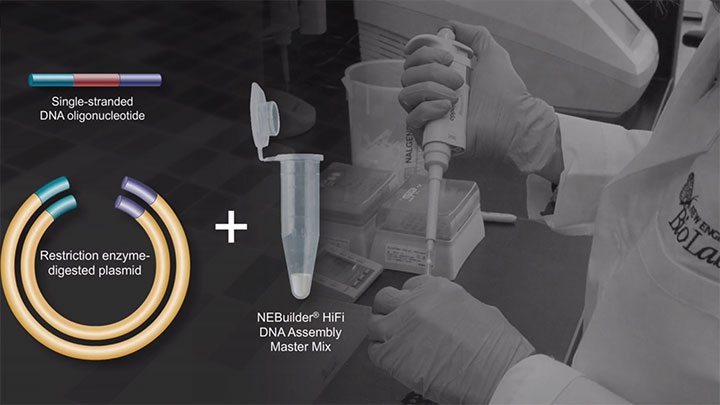
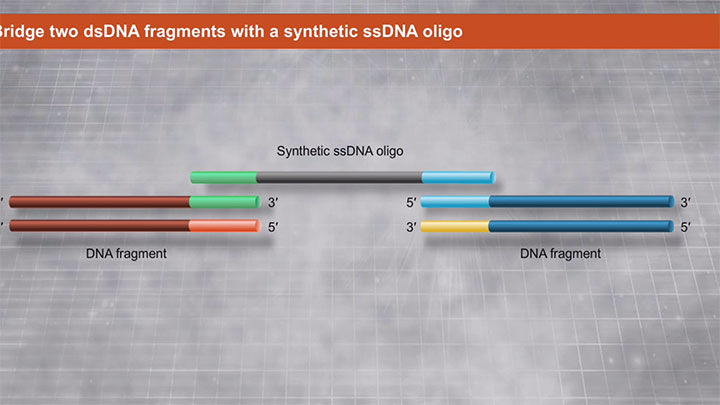
Single insert cloning to medium complexity assemblies of 2-6 fragments; single-stranded oligo(s) to dsDNA bridge assembly; single or multi-site mutagenesis |
Single insert cloning to highly complex assemblies of up to 30 fragments; sequences with high GC content and areas of repeats; dsDNA fragments < 100 bp |
|
PRIMER DESIGN |
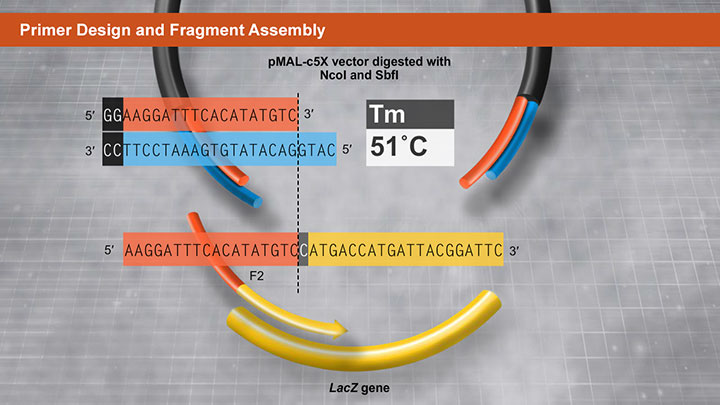
15-30 bp overlaps for all fragment lengths and number of fragments. Supported by online primer design tool. |
3-4 bp(4) unique overhangs/overlaps with Type IIS recognition site. Supported by online primer design and ligase fidelity tools. |
(1) The minimum recommended size for assembly of dsDNA fragments is 120 bp. For <100 bp fragments, single-stranded DNA oligos can be used.
(2) 50 bp to 10 kb have been validated internally. Sizes outside this range are possible.
(3) 50+ fragment assemblies require significant optimization. See Pryor et al (2022). Up to 30 fragments are recommended for routine assemblies and optimal performance.
(4) Overhang length depends on choice of Type IIS restriction enzyme.
Choose Type:
- Golden Gate Assembly Protocol for Using NEBridge® Golden Gate Assembly Kit (BsaI-HF®v2) (NEB #E1601)
- Recommended Screening Protocols for Using NEBridge Golden Gate Assembly Kit (BsaI-HFv2)
- Transformation Protocol for Using NEBridge Golden Gate Assembly Kit (BsaI-HFv2) (E1601)
- NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly Reaction Protocol (NEB #E2621, #E5520, #E2623)
- NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly Transformation Protocol
- NEBuilder Assembly of a PCR Fragment
- Protocol for Bridging double-stranded DNA with a single-stranded DNA oligo using NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly (NEB #E2621)
- Golden Gate Assembly Protocol for NEBridge® Ligase Master Mix (NEB #M1100)
- 24-Fragment Golden Gate Assembly using BsaI-HF®v2 (NEB #R3733)
- 52-Fragment Golden Gate Assembly using BsaI-HF®v2 (NEB #E1601)
- Golden Gate Assembly Protocol for Using NEB Golden Gate Assembly Mix (E1600)
- Recommended Screening Protocols for NEBridge Golden Gate Assembly Kit (BsmBI-v2) (NEB #E1602)
- 35-Fragment Golden Gate Assembly using BsmBI-v2 (NEB #E1602)
- Protocol for assembling annealed DNA oligonucleotides and a double-stranded DNA vector using NEBuilder HiFi DNA Assembly (NEB #E2621)
- Golden Gate Assembly Protocol using PaqCI® (NEB #R0745) and NEBridge Ligase Master Mix (NEB #M1100)
- Improved methods for site-directed mutagenesis using NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix
- Improved method for assembly of linear yeast expression cassettes using NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly Master Mix
- Construction of an sgRNA-Cas9 expression vector via single-stranded DNA oligo bridging of double-stranded DNA fragments
- Nanoliter Scale DNA Assembly Utilizing the NEBuilder HiFi Cloning Kit with the Labcyte Echo 525 Liquid Handler
- Accelerating DNA Construction to Protein Expression A Rapid 1-Day Workflow Using NEBridge Golden Gate Assembly
- DNA Shuffling using NEBridge® Golden Gate Assembly for Protein Engineering
-
Synthetic Genomics: Building a Better Bacterium
-
Restriction Endonucleases: Molecular Cloning and Beyond
- Molecular Cloning Technical Guide
- Synthetic Biology/DNA Assembly Selection Chart
- PCR Troubleshooting Guide
- Troubleshooting Guide for Cloning
- Troubleshooting Tips for Ligation Reactions
- Expanded “assembly standards” for MoClo, GoldenBraid2.0 and other modular Golden Gate Assembly methods
- Optimization Tips for NEBuilder® HiFi DNA Assembly and NEB® Gibson Assembly
- Technical Tips For Optimizing Golden Gate Assembly Reactions
Feature Articles
Brochures
Selection Tools
Troubleshooting Guides
Usage Guidelines
- Anton, B.P., Morgan, R.D., Ezraty, B., Manta, B., Barras, F., Berkmen, M. (2019) Complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli BE104, an MC4100 drivative lacking the methionine reductive pathway Microbiol Resour Announc; 8 (29), e00721-19. PubMedID: 31296691, DOI: 10.1128/MRA.00721-19
- Potapov, V., Ong, J.L., Kucera, R.B., Langhorst, B.W., Bilotti, K., Pryor, J.M., Cantor, E.J., Canton, B., Knight, T.F., Evans, T.C., Lohman, G.J.S. (2018) Comprehensive profiling of four base overhang ligation fidelity by T4 DNA ligase and application to DNA assembly ACS Synth Biol; 7 (11), PubMedID: 30335370, DOI: 10.1021/acssynbio.8b00333
- Feng Y, Zhang S, Huang X (2014) A robust TALENs system for highly efficient mammalian genome editing Sci Rep; 4, 3632. PubMedID: 24407151, DOI: 10.1038/srep03632
- Binder A, Lambert J, Morbitzer R, Popp C, Ott T, Lahaye T, Parniske M (2014) A Modular Plasmid Assembly Kit for Multigene Expression, Gene Silencing and Silencing Rescue in Plants PLoS One; 9(2), e88218. PubMedID: 24551083, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088218
- Abil Z, Denard CA, Zhao H (2014) Modular assembly of designer PUF proteins for specific post-transcriptional regulation of endogenous RNA J Biol Eng; 8(1), 7. PubMedID: 24581042, DOI: 10.1186/1754-1611-8-7
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.
Need more help selecting
a product for DNA assembly?
View our Synthetic Biology/DNA Assembly Selection Chart for more details.
Learn more about automation for cloning
With automation, researchers can scale up and increase throughput, as well as save time and money with rapid workflows.
Learn MoreWhich molecular cloning
technique is best for you?
For the new cloner, NEB suggests choosing one of three cloning methods. Find the method that works for your application.