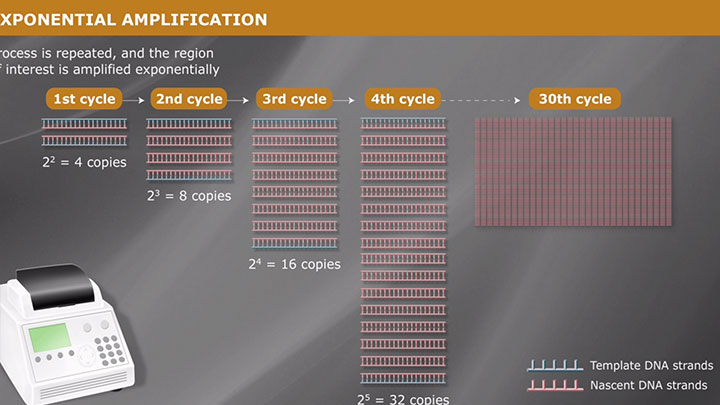
DNA Amplification, PCR & qPCR
Despite the ubiquitous nature of PCR and qPCR, it may not be the best option for all amplification needs. For point of care and other diagnostic applications, sequence-specific isothermal amplification methods, that eliminate the need for thermocycling, have been particularly useful. Instead of heat, these methods typically employ a strand-displacing DNA polymerase, like Bst DNA Polymerase, Large Fragment, to separate duplex DNA. To address some of the limitations of current isothermal amplification techniques, NEB has developed the next generation Bst, Bst 2.0 and a WarmStart® version of this enhanced polymerase, which enables room temperature reaction setup, yet is fully active at temperatures greater than 50°C.
RNA molecules can also be detected and manipulated through amplification via the use of reverse transcriptases (RT), which are RNA-dependent DNA Polymerases. RTs polymerize a strand of DNA that is complimentary to the original RNA template and is referred to as cDNA. This cDNA can then be further amplified through PCR, qPCR or isothermal methods as outlined above or detected in a single reaction using one-step RT-qPCR or RT-LAMP.
Nucleic acid amplification is a foundational process in molecular biology and, as a testament to its utility, new protocols and modifications are being developed constantly. At NEB, our goal is to use our understanding of enzymology, and dedication to providing high-quality products, to offer reagents for all of your applications. Please visit the application pages below to learn more.
TaqMan® is a registered trademark of Roche Molecular Systems, Inc.
SYBR® is a registered trademark of Molecular Probes, Inc.
Choose Type:
- Isothermal Amplification
- Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification
- Whole Genome Amplification & Multiple Displacement Amplification
- Strand Displacement Amplification & Nicking Enzyme Amplification Reaction
- Helicase-dependent Amplification
- Recombinase Polymerase Amplification and SIBA
- Nucleic Acid Sequenced Based Amplification and Transcription Mediated Amplification
- PCR
- Routine PCR
- High-Fidelity PCR
- PCR & Reaction Cleanup
- Polymerases for DNA Manipulation
- qPCR & RT-qPCR
- Dye-based qPCR & RT-qPCR
- Probe-based qPCR & RT-qPCR
- RT-PCR & cDNA Synthesis
- cDNA Synthesis
- RT-PCR
- Site Directed Mutagenesis
- Specialty PCR
- Extraction-Free PCR
- Hot Start PCR
- Long Range PCR
- Fast PCR
- Multiplex PCR
- Bisulfite Sequencing
- Polymerases for NGS Library Preparation
- Whole Genome Amplification
- PCR Using NEBNext® High-Fidelity 2X PCR Master Mix (M0541)
- PCR Using Q5® Hot Start High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (M0493)
- Protocol for Q5® Hot Start High-Fidelity 2X Master Mix
- Protocol for Q5® High-Fidelity 2X Master Mix
- PCR Optimization (E0555)
- Protocol for a Routine PCR (E0555)
- PCR Using Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (M0491)
- Protocol for a PCR reaction using NEBNext® Q5® Hot Start HiFi PCR Master Mix (M0543)
- Luna® Universal qPCR Master Mix Protocol (#M3003)
- Luna® Universal One-Step RT-qPCR Kit Protocol (E3005)
- Luna® Universal Probe One-Step RT-qPCR Kit Protocol (E3006)
- Luna® Universal Probe qPCR Master Mix Protocol (M3004)
- Luna® Probe One-Step RT-qPCR Kit (No ROX) Protocol (NEB# E3007)
- Optimized Integration of New England Biolabs® Loop-mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Reagents with Axxin ISO Instruments
- Primer Monitor: an online tool to track SARS-CoV-2 variants that may impact primers used in diagnostic assays
- The Luna 4X RT-qPCR Mix and Luna SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR Multiplex Assay Kit enable high throughput, automated detection workflows
- Multiplex PCR using Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase
- Key considerations for optimal lyophilized reagent development
- Detection of the Omicron variant mutation at position 26,270 in the SARS-CoV-2 E gene using the SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Colorimetric LAMP Assay Kit
- Optimized conditions for the CDC Influenza SARS-CoV-2 (Flu SC2) Multiplex Assay using Luna One-Step RT-qPCR Reagents
- Accelerating DNA Construction to Protein Expression A Rapid 1-Day Workflow Using NEBridge Golden Gate Assembly
- Optimizing rapid isothermal workflow for SARS-CoV-2 with WarmStart® LAMP with UDG
- Multiplex real-time PCR detection of monkeypox virus using Luna® qPCR Reagents
- PCR Reagents Brochure
- Polbase
- DNA Polymerase Selection Chart
- Reverse Transcriptase Selection Chart
- Luna® One-Step RT-qPCR Troubleshooting Guide
- Luna® qPCR Troubleshooting Guide
- PCR Troubleshooting Guide
- General Guidelines for Successful RNA Purification Using the Monarch Total RNA Miniprep Kit
- Guidance on Choosing Sample Input Amounts when Using the Monarch Total RNA Miniprep Kit
- Guidelines for PCR Optimization with OneTaq® and OneTaq® Hot Start DNA Polymerases
- Guidelines for PCR Optimization with Taq DNA Polymerase
- Guidelines for PCR Optimization with Thermophilic DNA Polymerases
- Optimization Tips for Luna® One-Step RT-qPCR
- Optimization Tips for Luna® qPCR
- Molecular Diagnostics for Gastrointestinal Parasites and Impact on Intestinal Microbiota in Rural Agentinian Children (2015)
- Amplification Reagents for Molecular Diagnostics Applications (2017)
- Colorimetric LAMP: Visual Detection for Simple Diagnostics (2017)
- A Single-tube, Low Input Protocol for Long Read Sequencing (2019)
Brochures
Web Tools
Selection Tools
Troubleshooting Guides
Usage Guidelines
Posters
- Gardner, A.F., Jackson, K.M., Boyle, M.M., Buss, J.A., Potapov, V., Gehring, A.M., Zatopek, K.M., Correa, I.R., Jr., Ong, J.L., Jack. W.E. (2019) Therminator DNA polymerase: Modified nucleotides and unnatural substrates Front Mol Biosci; 6, 28. PubMedID: 31069234, DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2019.00028
- Poole, C.B., Sinha, A., Ettwiller, L., Apone, L., McKay, K., Panchapakesa, V., Lima, N.F., Ferreira, M.U., Wanji, S., Carlow, C.K.S (2019) In silico identification of novel biomarkers and development of new rapid diagnostic tests for the filarial parasites Mansonella perstans and Mansonella ozzardi Sci Rep; 9 (1), 10275. PubMedID: 31311985, DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-46550-9
- Vladimir Potapov, Jennifer L. Ong. (2017) Examining Sources of Error in PCR by Single-Molecule Sequencing. PLOS One; PubMedID: 28683110
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.