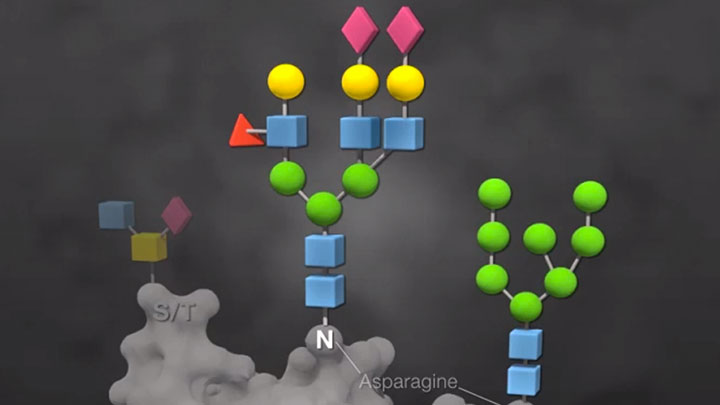
Recombinant Glycoprotein Expression
Choose Type:
- Which proteins are glycosylated?
- Is it possible to predict whether a protein is N- or O-glycosylated?
- Are heterologous proteins expressed with their canonical glycans, or with the glycans typical of the host?
- What are the differences between mammalian, yeast, insect (baculovirus), and plant cell expression systems?
- Will a mammalian glycoprotein be correctly glycosylated and folded if expressed in bacteria?
- What is the importance of the α-Gal and NGNA epitopes?
- Will each different protein expressed in a given system carry the same type of glycans?
- Will glycoproteins produced in yeast or plants be recognized by mammalian cells?
- O-Glycosidase Application Note 1 (P0733)
- O-Glycosidase (P0733)
- Endo-α-N-Acetylgalactosaminidase Application Note 1
- Protocol for α1-3,6 Galactosidase (P0731)
- Removal of terminal N-acetylglucosamine from the biantennary N-linked sugars of IgG
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α2-3,6,8 Neuraminidase (P0720)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-2 Fucosidase (P0724)
- Endo H/Endo Hf Protocol
- Typical Reaction Conditions (P0732)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β-N-Acetylhexosaminidasef (P0721)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β1-3 Galactosidase (P0726)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-6 Mannosidase (P0727)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-2,3 Mannosidase (P0729)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β1-4 Galactosidase (P0730)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-3,6 Galactosidase (P0731)
- Typical Reaction Conditions α-N-Acetylgalactosaminidase (P0734)
- Reaction Conditions for Remove-iT® PNGase F (P0706)
- Reaction Conditions for Endo S (P0741)
- Endo S Removal Magnetic Chitin Bead Protocol (P0741)
- Remove-iT® PNGase F Magnetic Chitin Bead Protocol (P0706)
- Reaction Conditions for Endo D (P0742)
- Endo D Removal Magnetic Chitin Bead Protocol (P0742)
- RNase B Deglycosylation Protocol (P7817)
- PNGase F Protocol
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β1-4 Galactosidase S (P0745)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α2-3,6,8,9 Neuraminidase A (P0722)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α2-3 Neuraminidase S (P0743)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase S (P0744)
- Rapid PNGase F Protocols (P0710)
- Intact Protein LS-ESI-TOF Protocol (P0710)
- Rapid PNGase F by SDS-PAGE Protocol (P0710)
- Glycan SPE C18 and Graphitized Carbon Protocols (P0710)
- Glycoproteomics: Buffer Exchange Protocols (P0710)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-3, 4, 6 Galactosidase (P0747)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-2, 3, 4, 6 Fucosidase (P0748)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-3, 4 Fucosidase (P0769)
- Rapid PNGase F Antibody Standard Protocol (P6043)
- Glycoproteomics: Buffer Exchange Protocols (P0711)
- Rapid PNGase F (non-reducing format) (P0711) Reaction Protocol
- Rapid PNGase F (non-reducing format) (P0711) SDS-PAGE Protocol
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β1-3,4 Galactosidase Reaction Protocol (P0746)
- Reaction Protocols for Protein Deglycosylation Mix II (P6044)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for Endo F3 Protocol (P0771)
- Reaction Conditions for PNGase A (P0707)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for a1-2,3,6 Mannosidase (P0768)
- Endo F2 Reaction Protocol (P0772)
- Removal of Endo F2 by Magnetic Beads (P0772)
-
The Structure, Function and Importance of Carbohydrates
Read about the structure, function, and importance of Carbohydrates from biology experts at NEB.
- Glycobiology Unit Conversion Chart
Feature Articles
Usage Guidelines
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.