Cellular Analysis
Choose Type:
-
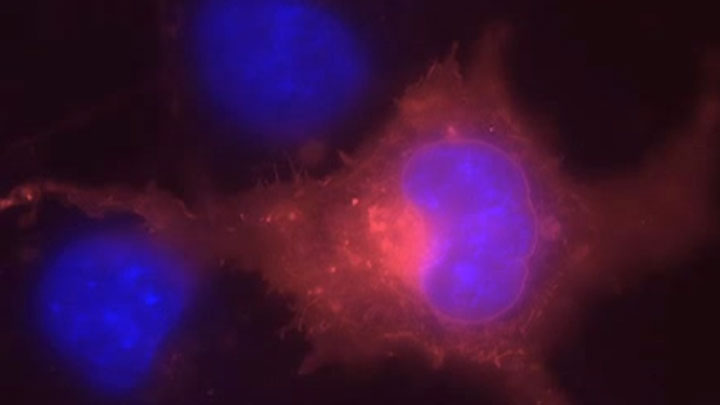
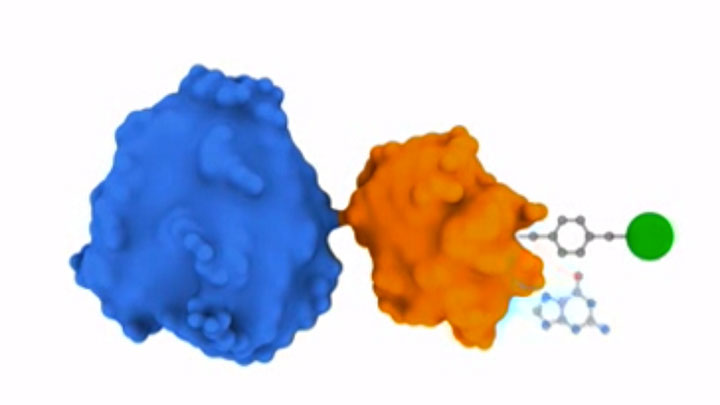
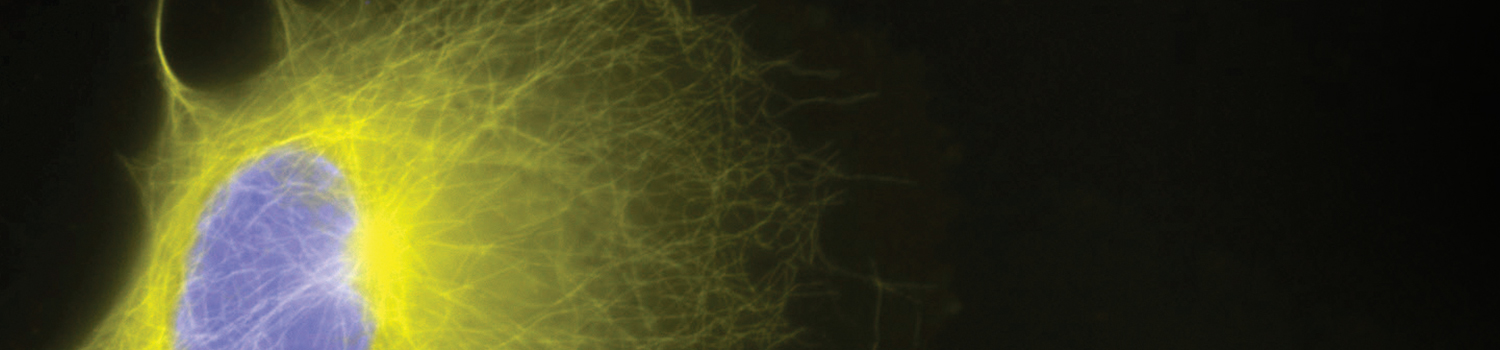
SNAP-tag® Technologies: Tools to Study Protein Function
Read about the NEB’s set of protein tools for the specific labeling (SNAP-, CLIP-, ACP- and MCP-tags) of fusion proteins.
-
Gaussia and Cypridina Luciferases - Ultrasensitive secreted reporters and their use in dual assays
- Cellular Imaging & Analysis Brochure
- Comparison of SNAP-tag®/CLIP-tag™ Technologies to GFP
- Labeling with SNAP-tag® Technology Troubleshooting Guide
- In Vitro Reconstitution of Thermococcus Species 9°N Okazaki Fragment Maturation (2015)
- One Ring To Bind Them All: Is HemeBiosynthesis A Factor In Wolbachia-Filarial Nematode Endosymbiosis? (2015)
- Genome-wide profiling of nuclease protected domains reveals physical properties of chromatin (2019)
- Improving Transcriptome Profiling for Single Cell and Low Input RNA (2019)
Feature Articles
Brochures
Selection Tools
Troubleshooting Guides
Posters
- Maffei, M., Morelli, C., Graham, E., Patriarca, S., Donzelli, L., Doleschall, B., de Castro, Reis, F., Nocchi, L., Chadick, C.H., Reymond, L., Correa, I.R., Jr., Johnsson, K., Hackett, J.A., Heppenstall, P.A (2019) A ligand based system for receptor specific delivery of proteins Sci Rep; 9(1), 19214.. PubMedID: 31844114, DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-55797-1
- Reuter, W.H., Masuch, T., Ke, N., Lenon, M., Radzinski, M., Van Loi, V., Ren, G., Riggs, P., Antelmann, H., Reichmann, D., Leichert, L.I., Berkmen, M (2019) Utilizing redox-sensitive GFP fusions to detect in vivo redox changes in a genetically engineered prokaryote Redox Biol; 26, 101280. PubMedID: 31450103, DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101280
- Carpinone, E.M., Li, Z., Mills, M.K., Foltz, C., Brannon, E.R., Carlow, C.K.S., Starai, V.J. (2018) Identification of putative effectors of the Type IV secretion system from the Wolbachia endosymbiont of Brugia malayi PLoS One; 13 (9), e0204736. PubMedID: 30261054, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204736
- Ke, N., Landgraf, D., Paulsson, J. and Berkmen, M. (2016) Visualization of Periplasmic and Cytoplasmic Proteins with a Self-Labeling Protein Tag. J Bacteriol; Jan 19;198(7), 1035-43. PubMedID: 26787765
- Domoszlai T, Martincuks A, Fahrenkamp D, Schmitz-Van de Leur H, Küster A, Müller-Newen G (2014) Consequences of the disease-related L78R mutation for dimerization and activity of STAT3 J Cell Sci; 127(Pt 9), 1899-910. PubMedID: 24569879, DOI: 10.1242/jcs.137422
- Johnson K. (2008) SNAP-tag Technologies: Novel tools to study protein function NEB Expressions ; 3.3 , 1-3 .
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.