NEBNext® Ultra™ II Directional RNA Library Prep
Library Preparation with FFPE RNA
While sufficient yield of a library is required for successful sequencing, quantity alone is not enough. The quality of a library is also critical, regardless of the input amount, quality or GC content of the sample RNA. A high-quality library will have uniform representation of the RNA of interest, minimal levels of ribosomal RNA, and strong strand-specificity. Ideally, the library will have high library complexity and excellent transcript coverage.
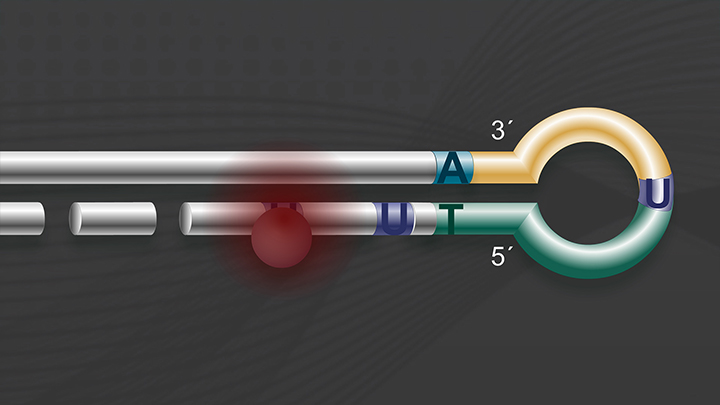
Importance of strand-specificity/directionality
Strand-specific/directional methods for sequencing RNA provide information on the DNA strand from which the RNA strand was transcribed. This is useful for many reasons including:
- Identification of antisense transcripts
- Determination of the transcribed strand of noncoding RNAs
- Measurement of expression levels of coding or noncoding overlapping transcripts
- Overall, the ability to determine the originating strand can substantially enhance the value of a RNA-seq experiment.
The NEBNext Ultra II Directional RNA Library Prep Kit derives its directionality from the “dUTP method" for strand-specificity, with proven superiority for this application (1).
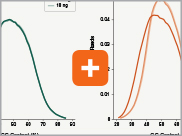
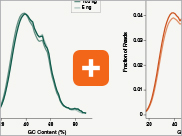
Uniform GC content distribution
A high quality library will have uniform representation of the original sample, including uniform coverage across the GC spectrum, regardless of the input amount of the sample. With lower input amounts, more PCR cycles are required and this has the potential to introduce bias, including GC bias. The increased efficiencies of each step in the Ultra II Directional RNA library prep workflow reduce the number of PCR cycles required. This, combined with the use of Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase for library amplification, ensures excellent GC content distribution for a wide range of input amounts for Ultra II Directional RNA libraries.
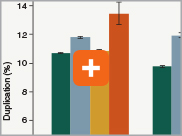
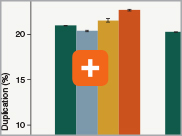
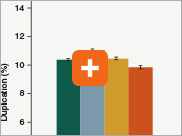
Minimizing duplication rates
Duplication rates (the percentage of sequence reads due to PCR duplicates) can increase when libraries lack complexity, and are more common with low input libraries when more PCR cycles are used. The increased efficiencies of each step in the Ultra II Directional RNA library prep workflow and the reduced number of PCR cycles increase the library complexity for low input amounts.
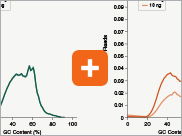
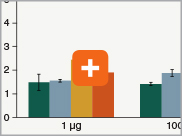
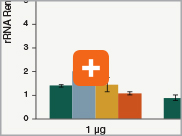
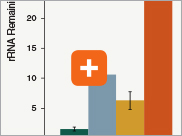
Levels of ribosomal RNA levels remaining
Since the majority (>90%) of RNA in a sample can be ribosomal RNA (rRNA), it must be removed prior to library preparation. When only mRNA is of interest, and the sample is high-quality eukaryotic RNA, oligo dT-based enrichment of intact poly(A) mRNA tails is the method of choice. However, when the sample quality is lower (and therefore poly(A) tails may not be intact), the RNA of interest goes beyond just mRNA, or the sample is not eukaryotic and therefore lacks a poly(A) tail, depletion of rRNA can be performed. The NEBNext Ultra II Directional RNA Library Prep Kit is compatible with both Poly(A) mRNA enrichment and rRNA depletion workflows, and libraries can be generated with as little as 10 ng Total RNA (poly(A) mRNA enrichment workflow) or 5 ng Total RNA (rRNA depletion workflow). Effective removal of rRNA is achieved with both workflows.
1. Levin, J.Z., et al. (2010) Nature Methods. 7, 709–715.
Available kits:
|
NEBNext® Ultra™ II Directional RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina® |
|
|
NEBNext® Ultra™ II Directional RNA Library Prep with Sample Purification Beads |