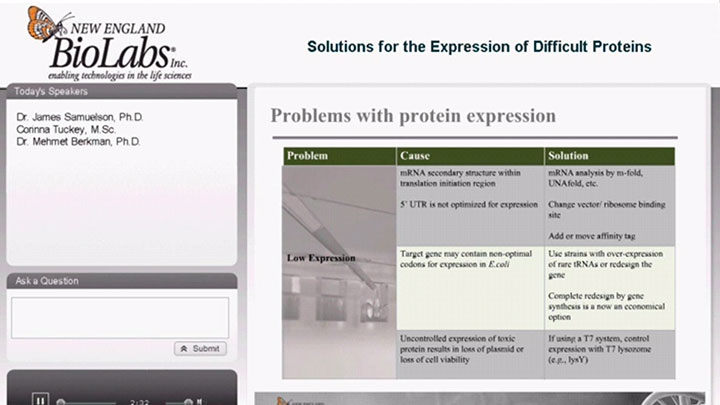
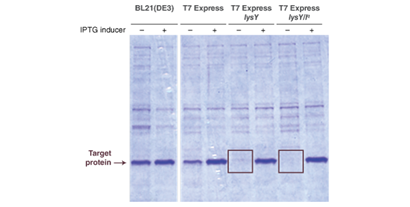
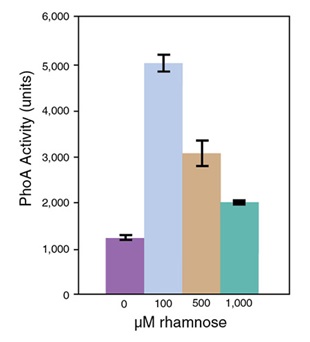
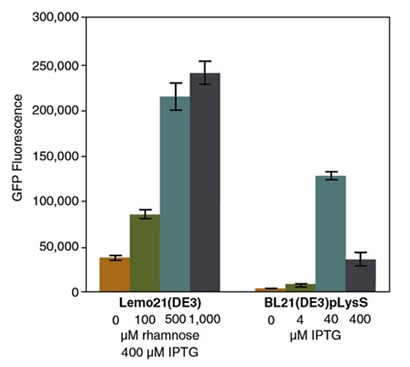
Toxic Protein Expression
Choose Type:
- Protein Synthesis Reaction using PURExpress (E6800)
- Protocol for Expression Using T7 Express lysY/Iq (C3013)
- Protein Expression with T7 Express strains
- Protein Expression Using Lemo21(DE3) (C2528)
- High Efficiency Transformation Protocol (C3013)
- High Efficiency Transformation Protocol (C3016)
- Determination of Protein Synthesis Yield with PURExpress (E3313, E6800, E6840, E6850)
- Protocol for Expression Using T7 Express lysY (C3010)
- Protocol for Expression Using T7 Express Iq (C3016)
- Purification of Synthesized Protein using Reverse His-tag Purification
- Transformation Protocol (C2528)
- Analysis of Synthesized Protein using PURExpress (E6800)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C2528)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C3016)
- Measurement of 35S-Methionine Incorporation by TCA Precipitation and Yield Determination using PURExpress
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C3013)
- High Efficiency Transformation Protocol (C3010)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C3010)
- Expression Using SHuffle (C3026)
- E coli Lemo21 DE3 A T7 RNA Polymerase-based protein overexpression platform for routine and difficult targets
- Intein-Mediated Protein Ligation IPL and Labeling with the IMPACT™ Kit
- Protein Expression with T7 Express Strains
- Use of the PURExpress® in vitro Protein Synthesis Kit, Disulfide Bond Enhancer and SHuffle® Competent E. coli for heterologous in vitro and in vivo cellulase expression.
-
Avoid Common Obstacles in Protein Expression
Read how to avoid common obstacles in protein expression that prevent interactions with cellular machinery.
-
The Future of Cell-Free Protein Synthesis
Cell-free protein synthesis has the potential to become one of the most important high throughput technologies for functional genomics and proteomics.
- Competent Cell Brochure
- Protein Expression & Purification Brochure
- DNA Sequences and Maps Tool
- Competent Cell Product Comparison
- Protein Expression and Purification Selection Chart
Feature Articles
Brochures
Web Tools
Selection Tools
E. coli Hosts
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.