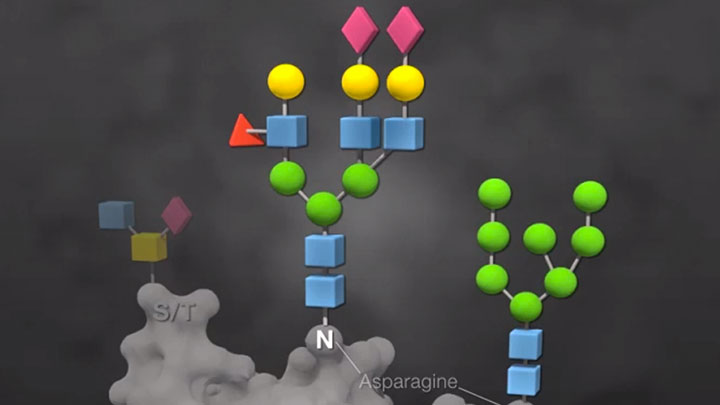
Glycoprotein Analysis
Choose Type:
- What are Glycosidases and their uses?
- What is a good endoglycosidase substrate?
- Can endoglycosidases be removed from the reaction?
- Can glycosidases be used in combination for extensive digestion?
- Do I need to deglycosylate my protein sample for proteomic analysis?
- Do the Remove-iT glycosidases have the same specificity as enzymes without a tag?
- What happens to my protein after deglycosylation?
- Does enzymatic N-and O-glycan removal preserve protein structural integrity and function?
- O-Glycosidase Application Note 1 (P0733)
- O-Glycosidase (P0733)
- Endo-α-N-Acetylgalactosaminidase Application Note 1
- Protocol for α1-3,6 Galactosidase (P0731)
- Removal of terminal N-acetylglucosamine from the biantennary N-linked sugars of IgG
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α2-3,6,8 Neuraminidase (P0720)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-2 Fucosidase (P0724)
- Endo H/Endo Hf Protocol
- Typical Reaction Conditions (P0732)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β-N-Acetylhexosaminidasef (P0721)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β1-3 Galactosidase (P0726)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-2,3 Mannosidase (P0729)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β1-4 Galactosidase (P0730)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-3,6 Galactosidase (P0731)
- Typical Reaction Conditions α-N-Acetylgalactosaminidase (P0734)
- Reaction Conditions for Remove-iT® PNGase F (P0706)
- Reaction Conditions for Endo S (P0741)
- Endo S Removal Magnetic Chitin Bead Protocol (P0741)
- Remove-iT® PNGase F Magnetic Chitin Bead Protocol (P0706)
- Reaction Conditions for Endo D (P0742)
- Endo D Removal Magnetic Chitin Bead Protocol (P0742)
- RNase B Deglycosylation Protocol (P7817)
- PNGase F Protocol
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β1-4 Galactosidase S (P0745)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α2-3,6,8,9 Neuraminidase A (P0722)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α2-3 Neuraminidase S (P0743)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β-N-Acetylglucosaminidase S (P0744)
- Rapid PNGase F Protocols (P0710)
- Intact Protein LS-ESI-TOF Protocol (P0710)
- Rapid PNGase F by SDS-PAGE Protocol (P0710)
- Glycan SPE C18 and Graphitized Carbon Protocols (P0710)
- Glycoproteomics: Buffer Exchange Protocols (P0710)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-3, 4, 6 Galactosidase (P0747)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-2, 3, 4, 6 Fucosidase (P0748)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for α1-3, 4 Fucosidase (P0769)
- Rapid PNGase F Antibody Standard Protocol (P6043)
- Glycoproteomics: Buffer Exchange Protocols (P0711)
- Rapid PNGase F (non-reducing format) (P0711) Reaction Protocol
- Rapid PNGase F (non-reducing format) (P0711) SDS-PAGE Protocol
- Typical Reaction Conditions for β1-3,4 Galactosidase Reaction Protocol (P0746)
- Reaction Protocols for Protein Deglycosylation Mix II (P6044)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for Endo F3 Protocol (P0771)
- Reaction Conditions for PNGase A (P0707)
- Typical Reaction Conditions for a1-2,3,6 Mannosidase (P0768)
- Endo F2 Reaction Protocol (P0772)
- Removal of Endo F2 by Magnetic Beads (P0772)
- a1-2,4,6 Fucosidase O Digestion of Released Labeled Glycans Protocol
-
Using Glycosidases to Remove Trim or Modify Glycans on Therapeutic Protein
-
N-Glycan Composition Profiling for Quality Testing of Biotherapeutics
Feature Articles
- Vainauskas, S., Kirk, C.H., Petralia, L., Guthrie, E.P., McLeod, E., Bielik, A., Luebbers, A., Foster, J.M., Hokke, C.H., Rudd, P.M., Shi, X., Taron, C.H (2018) A novel broad specificity fucosidase capable of core a1-6 fucose release from N-glycans labeled with urea-linked fluorescent dyes Sci Rep; PubMedID: 29934601, DOI: 1038/s41598-018-27797-0
- Albrecht, S., Vainauskas, S., Stöckmann, H., McManus, C., Taron, C.H. and Rudd, P.M. (2016) Comprehensive Profiling of Glycosphingolipid Glycans Using a Novel Broad Specificity Endoglycoceramidase in a High-Throughput Workflow. Anal Chem; May 3;88(9), 4795-802. Anal Chem.. PubMedID: 27033327
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.