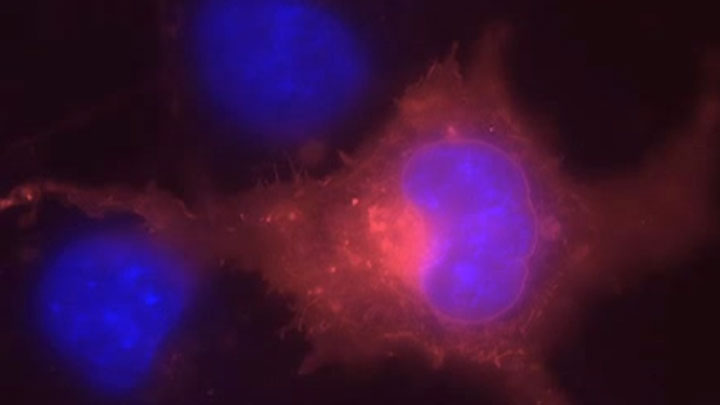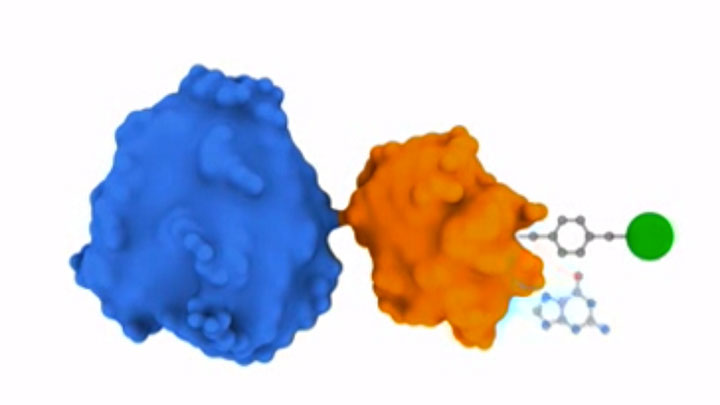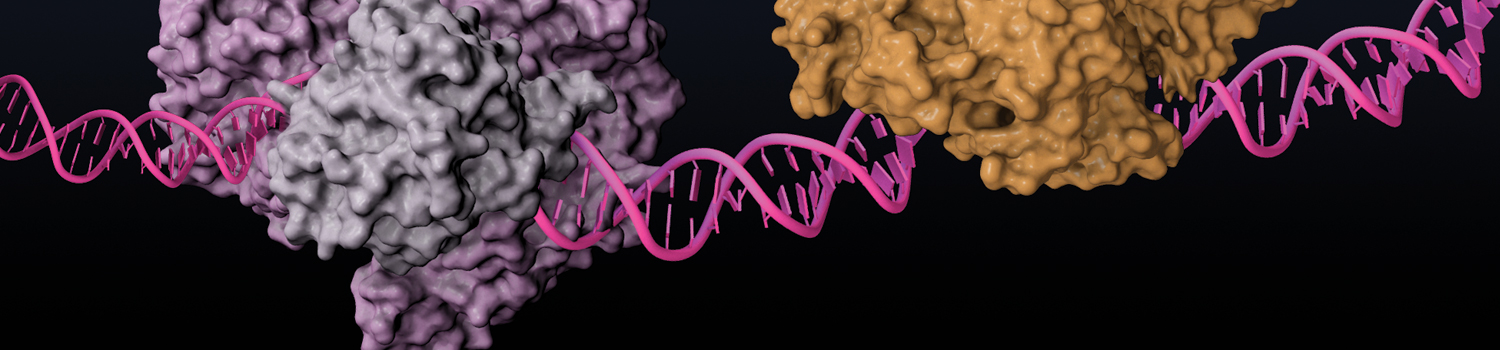
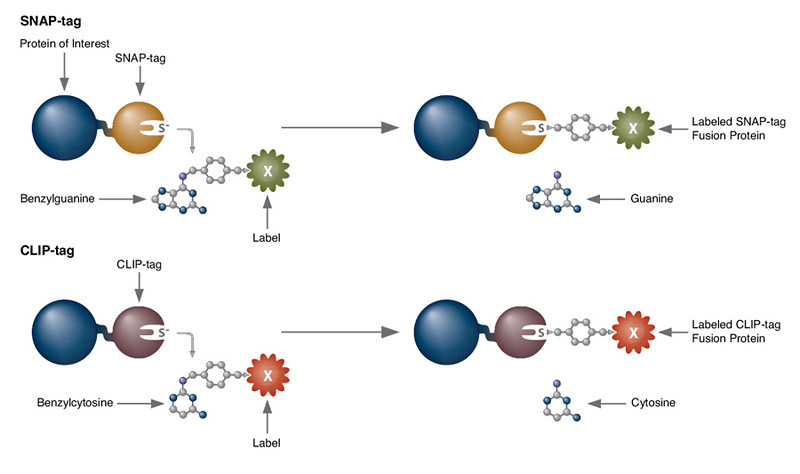
Protein Labeling
Choose Type:
- Affinity Purification and On-column Cleavage (E6901)
- Cellular Labeling (E9100)
- Cellular Labeling (E9230)
- Cellular Labeling (S9103)
- Cellular Labeling (S9104)
- Cellular Labeling (S9105)
- Cellular Labeling (S9107)
- Cellular Labeling (S9109)
- Cellular Labeling (S9110)
- Cellular Labeling (S9112)
- Cellular Labeling (S9124)
- Cellular Labeling (S9129)
- Cellular Labeling (S9132)
- Cellular Labeling (S9134)
- Cellular Labeling (S9136)
- Cellular Labeling (S9217)
- Cellular Labeling (S9219)
- Cellular Labeling (S9232)
- Cellular Labeling (S9233)
- Cellular Labeling (S9234)
- Cloning of CLIP-tag Fusions in pCLIPf (N9215)
- CoA 488 (S9348)
- Construction of the Fusion Plasmid (E6901)
- Expression of CLIP-tag Fusions (N9215)
- Fusion Protein Expression (E6901)
- Cellular Labeling (S9101)
- Instructions for Use with ACP Synthase (P9301)
- Instructions for Use with SFP Synthase (P9302)
- Labeling CLIP-tag Fusion Proteins with BC-substrates (S9236)
- Labeling Mammalian Cell Lysates (S9147)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9110)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (P9302)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9103)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9104)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9105)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9106)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9107)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9109)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9143)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9217)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9219)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9220)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9221)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9232)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9233)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9234)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (P9301)
- Instructions for Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9348)
- Labeling of Proteins in Solution (E9230)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9101)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9351)
- Labeling on the Surface of Cells (S9349)
- Labeling on the Surface of Cells (S9350)
- Labeling on the Surface of Cells (S9351)
- Labeling Proteins in vitro (S9112)
- Labeling Proteins in vitro (S9124)
- Labeling Proteins in vitro (S9129)
- Labeling Proteins in vitro (S9132)
- Labeling Proteins in vitro (S9134)
- Labeling Proteins in vitro (S9136)
- Labeling Proteins in vitro (S9147)
- Labeling SNAP-tag Fusion Proteins with BG-substrates (S9150)
- Labeling SNAP-tag Fusion Proteins with BG-substrates (S9151)
- Labeling SNAP-tag Purified Protein In Vitro (P9312)
- Preparation of Media and Solutions (E6901)
- Primer Design for Restriction Enzyme Cloning (E6901)
- Protocol for Anti-SNAP-tag® Antibody (Polyclonal) (P9310)
- Simplified Expression and Purification Protocol (E6901)
- Use of SNAP-Cell Block with SNAP-Cell Substrates (E9100)
- Use of CLIP-Cell Block with CLIP-Cell Substrates (E9230)
- Use with CLIP-tag substrates (S9220)
- View the video "Fluorescent Labeling of COS-7 Expressing SNAP-tag Fusion Proteins for Live Cell Imaging" in the Journal of Visualized Experiments (JoVE)
- Cellular Labeling (E9120)
- Instructions for Cellular Labeling (E9200)
- Labeling Proteins in vitro (E9120)
- Labeling Proteins in vitro (E9200)
- Cloning of SNAP-tag Fusions in pSNAPf (N9183)
- Cloning of SNAP-tag Fusions in pSNAP-tag(T7)-2 (N9181)
- Expression of SNAP-tag Fusions (N9181)
- Expression of SNAPf Fusions (N9183)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9349)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9350)
- Labeling SNAP-tag Fusion Proteins with BG-substrates (S9148)
- Protocol for Labeling SNAP-tag Fusion Proteins with BG-substrates (S9153)
- Cellular Labeling (S9221)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (E9100)
- Use with SNAP-Surface substrates (S9143)
- Reaction Conditions for Chemical Coupling (S9148)
- Reaction Conditions for Chemical Coupling (S9153)
- Use SNAP-Capture Magnetic Beads (S9145)
- Use SNAP-Capture Pull Down Resin (S9144)
- Reaction Conditions for Chemical coupling (S9150)
- Reaction Conditions for Chemical Coupling (S9151)
- Reaction Conditions for Chemical Coupling (S9236)
- Use with SNAP-Cell Substrates (S9106)
- Cellular Labeling (S9159)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9159)
- Fusion Constructs (E6901)
- Cellular Labeling (S9102)
- Labeling of Proteins in vitro (S9102)
-
SNAP-tag® Technologies: Tools to Study Protein Function
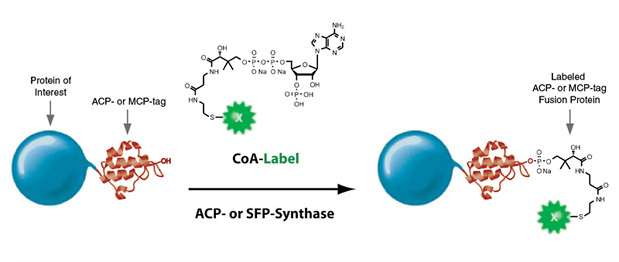
Read about the NEB’s set of protein tools for the specific labeling (SNAP-, CLIP-, ACP- and MCP-tags) of fusion proteins.
- Cellular Imaging & Analysis Brochure
- Comparison of SNAP-tag®/CLIP-tag™ Technologies to GFP
- Labeling with SNAP-tag® Technology Troubleshooting Guide
Feature Articles
Brochures
Selection Tools
Troubleshooting Guides
- Clone and express once, then use with a variety of substrates
- Non-toxic to living cells
- Wide selection of fluorescent substrates
- Highly specific covalent labeling
- Simultaneous dual labeling
- Simultaneous dual protein labeling inside live cells
- Protein localization and translocation
- Pulse-chase experiments
- Receptor internalization studies
- Selective cell surface labeling
- Protein pull-down assays
- Protein detection in SDS-PAGE
- Flow cytometry
- High throughput binding assays in microtiter plates
- Biosensor interaction experiments
- FRET-based binding assays
- Single molecule labeling
- Super-resolution microscopy
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.