
Superior error detection using Authenticase® enhances assembled gene synthesis
Posted on Tuesday, September 5, 2023
By
Topic: What is Trending in Science, Tips for the lab
Gene synthesis workflows frequently encounter the challenge of residual errors in DNA fragments, necessitating a search for efficient error detection and reduction strategies. In many gene synthesis workflows, users obtain fragments for assembly by purchasing synthesized dsDNA (e.g., gBlocks) or by preparing amplicons from overlapping oligos. Often, these fragments have residual errors arising directly from the oligonucleotides used to generate the fragments. While Sanger sequencing or next generation sequencing can be used to detect these errors, it is labor-intensive and costly. It wastes time at the bench picking and sequencing every single clone to find the correct one. The key lies in reducing errors in your pool of synthesized fragments upfront, which will ultimately reduce your sequencing burden.
Eliminating mismatches in DNA with structure-specific enzymes
Structure-specific enzymes can eliminate the DNA errors introduced during gene synthesis. These enzymes recognize structural perturbations introduced by mismatches, often appearing as "bubble" regions within the DNA structure. For a structure-specific enzyme to recognize the error, the DNA strands must look different – a mismatch must be created. If errors exist in the original oligo assembly pool, PCR amplification will copy the error and produce homoduplexes with errors on both strands. To remove these errors, the products of the PCR reaction must be denatured and re-annealed to allow heteroduplex formation between PCR products with and without mutations. At this point, a structure-specific enzyme can recognize and cleave the newly formed mismatches. Then, with the inclusion of a high-fidelity DNA polymerase, PCR amplification copies the error-depleted population, correcting many of the errors. As a result, you're left with a pool of amplicons containing fewer errors than in the original pool, which means fewer colonies to pick, screen and sequence.
Authenticase – the latest in NEB's molecular biology toolbox
The rigorous inquiry into enzyme functionality and application is something NEB scientists have been doing for 50 years. The potential to engineer, improve functionality, and broaden enzyme application regularly leads them to better molecular tools, robust and streamlined workflows, and more accurate results. The recent introduction of Authenticase (NEB #M0689) is another addition to the molecular biology toolbox that helps scientists work effortlessly through their screening experiments.

Figure 1: Authenticase cleaves dsDNA carrying mismatches or indels, leaving either 3´ or 5´ overhangs.
Figure 1 shows the action of Authenticase (NEB #M0689), a new, unique blend of structure-specific nucleases that can recognize and cleave outside mismatch and indel (insertion/ deletion) regions, ranging from 1-10 base pairs on double-stranded DNA. The methodology of creating mismatches that structure-specific enzymes can detect is not new, it has just been limited. Some enzymes are better at recognizing mismatches that contain a particular nucleotide. Others only recognize certain nucleotide combinations, but not all. The unique combination of enzymes in Authenticase gives it superior recognition capabilities. Authenticase identifies indels from 1-10 bp in length and seven of the eight possible single-base mismatch combinations: C/C, T/C, A/C, T/G, G/G, T/T and A/A. The only single-base mismatch it does not recognize is A/G.
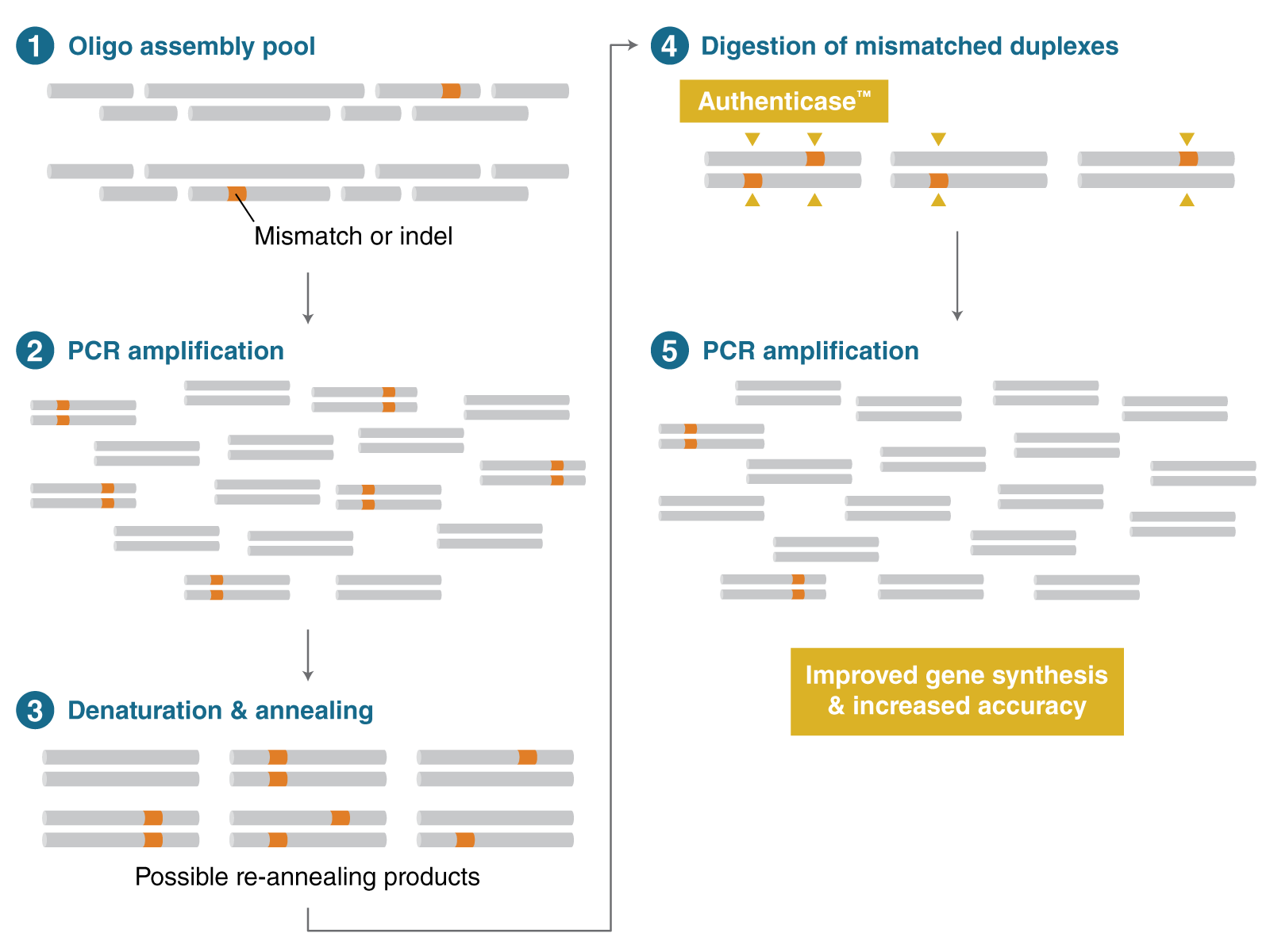
Figure 2: A straightforward protocol for correcting errors in oligo assembly pools using Authenticase. It is a mixture of structure-specific nucleases capable of recognizing and cleaving outside mismatch and indel regions, ranging from 1–10 basepairs (bp) on double-stranded DNA. Authenticase can be used as an error-correction reagent in oligo-based PCR gene assembly by enzymatically removing “mistakes” prior to the final renaturation and amplification step.
Following the detection of these mismatches and cleavage of the double-stranded DNA by Authenticase, PCR amplification with Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (NEB #M0491) corrects these errors. Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase has the highest-fidelity amplification available (280x that of Taq DNA Polymerase) and both 3´ and 5´ prime error-correction properties.
DNA mismatches can provide significant challenges if you're doing DIY gene synthesis, especially when implementing high-throughput approaches for large synthesis projects. Molecular tools and protocols that streamline and improve processes are invaluable to your workflow because they enhance productivity and reduce expenditure. The Authenticase mix of structure-specific nucleases increases the population of accurate fragments in the enzyme-corrected DNA pools and enriches the amplicons with more precision. The ability to remove errors before the final renaturation and amplification steps during gene synthesis results in enhanced DNA quality and accuracy.
Learn more about Authenticase, including protocols to correct errors during gene synthesis.
Note: Authenticase can also substitute T7 Endonuclease I in the mismatch detection assay used to assess the efficiency of genome editing.
NEB will not rent, sell or otherwise transfer your data to a third party for monetary consideration. See our Privacy Policy for details. View our Community Guidelines.
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. See www.neb.com/trademarks. The use of these products may require you to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
Don’t miss out on our latest NEBinspired blog releases!
- Sign up to receive our e-newsletter
- Download your favorite feed reader and subscribe to our RSS feed
Be a part of NEBinspired! Submit your idea to have it featured in our blog.


