T7 Expression
Choose Type:
- What are the strain properties (C2566)?
- Is T7 Express (NEB #C2566H and NEB #C2566I) compatible with auto-induction procedures?
- What are the strain properties (C2527)?
- What is the difference between T7 Express (NEB #C2566H/I) and BL21(DE3) (NEB #C2527H/I)?
- Can the NEBExpress Competent E.coli (High Efficiency) be used for the expression of constructs containing a T7 promoter?
-
Avoid Common Obstacles in Protein Expression
Read how to avoid common obstacles in protein expression that prevent interactions with cellular machinery.
- Competent Cell Brochure
- Protein Expression & Purification Brochure
- DNA Sequences and Maps Tool
- Competent Cell Product Comparison
- Competent Cell Selection Guide
Feature Articles
Brochures
Web Tools
Selection Tools
- Agrawal, A., Bisharyan, Y., Papoyan, A, Bednenko, J., Cardarelli, J., Yao, M., Clark, T., Berkmen, M., Ke, N., Colussi, P. (2019) Fusion to Tetrahymena thermophila granule lattice protein 1 confers solubility to sexual stage malaria antigens in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr Purif; 153, 7-17. PubMedID: 30081196, DOI: 10.1016/j.pep.2018.08.001.
- Leith, E.M., O'Dell, W.B., Ke, N., McClung, C., Berkmen, M., Bergonzo, C., Brinson, R.G., Kelman, Z (2019) Characterization of the internal translation initiation region in monoclonal antibodies expressed in Escherichia coli J Biol Chem; 294(48), 18046-18056.. PubMedID: 31604819, DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011008
- Reddy, P.T., Brinson, R.G., Hoopes, J.T., McClung, C., Ke, N., Kashi, L. (2018) Platform development for expression and purification of stable isotope labeled monoclonal antibodies in Escherichia coli. mAbs MAbs; 10 (7), 992-1002. PubMedID: 30060704, DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1496879
- Robinson, M.-P., Ke, N., Lobstein, J., Peterson, C., Szkodny, A., Mansell, T.J., Tuckey, C., Riggs, P.D., Colussi, P.A., Noren, C.J., Taron, C.H., Delisa, M.P., Berkmen, M. (2015) Efficient expression of full-length antibodies in the cytoplasm of engineered bacteria Nat Commun; (6)8072, PubMedID: 26311203, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9072.
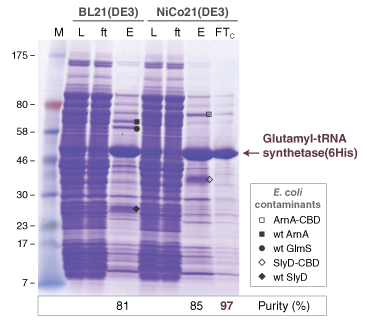
E. coli Hosts
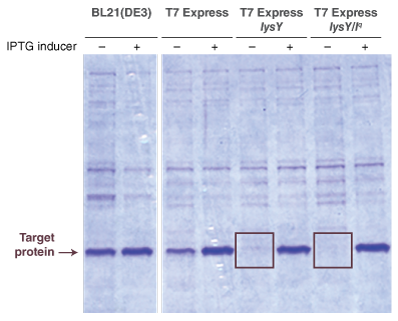
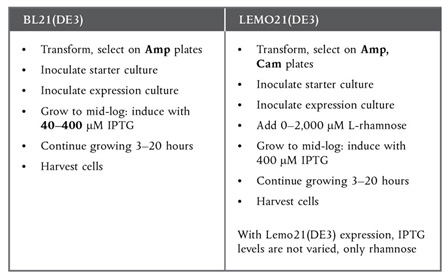
Protein expression with Lemo21(DE3) is very similar to BL21(DE3), with only a few minor changes.
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.

