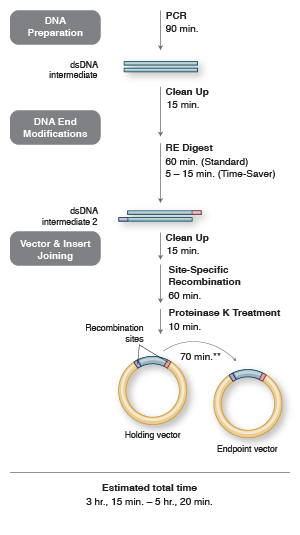
Recombinational Cloning
Return to Cloning & Synthetic BiologyTypically, a researcher would clone a sequence of interest into a holding vector ("Entry" for Gateway and "Donor" for Creator) using traditional cloning methods. Once the new clone is made, it is easily shuttled to many different "destination" or "acceptor" vectors that contain the appropriate sequence recognized by the recombinase (attachment sites attB and attP with Gateway and loxP with Creator/Echo). Higher throughput is possible with these systems and they have become a useful tool for screening many different expression hosts for protein expression projects or for multiple reporter vectors for functional analysis studies. At this time, only the Gateway system is still commercially supported, although NEB does sell Cre Recombinase (NEB #M0298), an essential reagent for the in vitro recombination step used by the Creator and Echo Cloning systems.
Advantages:- Allows high-throughput vector creation
- Widely available ORF collections
- Cost relative to traditional methods
- Vector sets typically defined by supplier
- Propietary enzyme mixes often required
Recombinational Cloning Workflow