Home
Reagents and Molecular Biology Products
Restriction Endonuclease Products
Restriction Endonucleases
Restriction Enzyme Quality
Restriction Enzyme Quality
Return to Restriction EndonucleasesNEB extensively quality controls its popular lines of standard and high-fidelity (HF®) restriction enzymes. Each new lot is tested and must meet the specifications designated for the product. Quality controls for restriction enzymes, both standard and HF, include:
- Physical Purity:
Enzymes are evaluated by SDS-PAGE gel to ensure the highest levels of purity and the absence of contaminating proteins. - Endonuclease Activity:
Using radioactively labeled DNA substrate and/or state-of-the-art capillary electrophoresis-based assays with fluorescently labeled substrates, NEB is able to detect very low levels of exonuclease activity. - Exonuclease Activity:
To ensure that there are no contaminating enzymes that could cause nicking or non-specific nuclease degradation, reagents are incubated with supercoiled plasmid DNA for 4 hours to demonstrate the absence of endonuclease contamination. - Non-specific DNase Activity:
Enzymes are incubated overnight with Lambda DNA to confirm that there is no additional non-specific nuclease activity present. - Cloning QC (Ligation & Re-cutting):
A DNA template is overdigested by the appropriate restriction enzyme, and the percentage of DNA fragments ligated and re-cut are determined by agarose gel electrophoresis. - Cloning QC (Blue-white Screening):
A DNA plasmid is over-digested by the appropriate restriction enzyme, and the linearized plasmid DNA is ligated and transformed into an E. coli strain with greater than 99% correct transformants, as determined by a blue-white screen. - Functional Test (15 minute Digest):
A 50 μl reaction containing 1 μg of DNA and 1 μl restriction enzyme incubated for 15 minutes results in complete digestion as determined by agarose gel electrophoresis. - DNA Contamination (E. coli Genomic):
Enzymes are screened for the presence of E. coli genomic DNA using SYBR® Green qPCR with primers specific for the E. coli 16S rRNA locus.
Restriction Enzyme Competitor Study: Nuclease Contamination
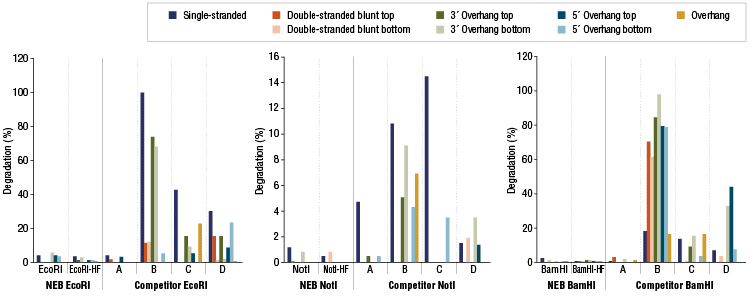
EcoRI, NotI, and BamHI from multiple suppliers were tested in reactions containing a fluorescent labeled single stranded, double stranded blunt, 3’overhang or 5’ overhang containing oligonucleotides. The percent degradation is determined by capillary electrophoresis and peak analysis. The resolution is at the single nucleotide level.

