Methylation Dependent Restriction Enzymes for Epigenetics
Choose Type:
- What's the difference between DpnI, DpnII, MboI, and Sau3AI?
- How much enzyme should be used for cleaving genomic DNA?
- Does McrBC cut hemi-methylated DNA?
- Are there any published papers in which McrBC has been used?
- Will DpnI cleave hemimethylated DNA?
- Is extended digestion of McrBC recommended?
- Why does my McrBC cleaved DNA smear when run on an agarose gel?
- Does McrBC produce blunt or sticky ends?
-
Epigenetics - Expanding on Genomic Foundations
- Epigenetics Brochure
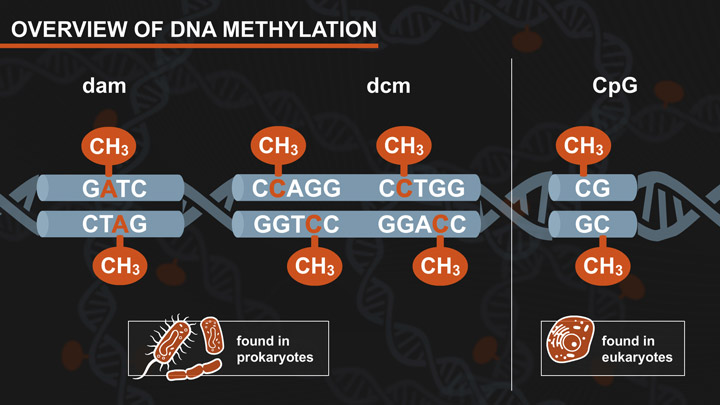
- Dam-Dcm and CpG Methylation
Feature Articles
Brochures
Selection Tools
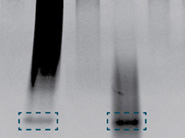
Note: Yeast DNA does not contain methylated DNA and thus, no 32-mer is detected.
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.