Phage Display
Choose Type:
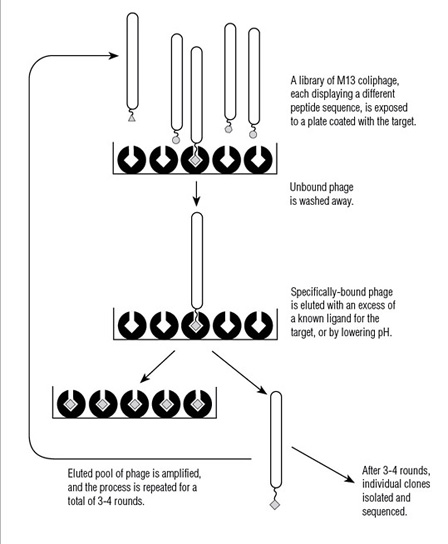
- What is Ph.D.™ Phage Display?
- Can a different bacterial strain be used with the Ph.D.™ Phage Display?
- When using the Ph.D.™ Phage Display, panning yielded a consensus sequence, but no ELISA signal.
- I am using Ph.D.™ Phage Display and the streptavidin control experiment did not yield the HPQ consensus sequence.
- No plaques are visible when titering using the Ph.D.™ Phage Display kit.
- All or most of the eluted phage plaques are white (colorless) on Xgal/IPTG plates.
- A synthetic peptide corresponding to an ELISA-positive sequence does not bind my target.
- Phage Display FAQs
- What peptide libraries are available for use with Ph.D.™ Phage Display?
- When performing an experiment using Ph.D.™ Phage Display, the ELISA indicates that background binding to the plate is as high as binding to the target.
-
Applications of the Ph.D. Phage Display Peptide Libraries
Feature Articles
- Li, L. et al. (2010) Peptide ligands that use a novel binding site to target both TGF-β receptors Mol Biosyst; 6, 2392-2402. PubMedID: 20890540
- Hairiri, G. et al. (2010) Radiation-guided drug delivery to mouse models of lung cancer Clin Cancer Res; 16, 4968-77. PubMedID: 20802016
- Jung, E. et al. (2010) Artificial neural network study on organ-targeting peptides J Comput Aided Mol Des; 24, 49-56. PubMedID: 20020181
- Liu, M. et al. (2010) D-peptide inhibitors of the p53-MDM2 interaction for targeted molecular therapy of malignant neoplasms Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A; 107, 14321-6. PubMedID: 20660730
- Balian, G. et al. (2010) Peptides from phage display library modulate gene expression in mesenchymal cells and potentiate osteogenesis in unicortical bone defects J Vis Exp; 46, PubMedID: 21178970
- Matsuo, A.L. et al. (2010) A novel melanoma-targeting peptide screened by phage display exhibits antitumor activity J Mol Med; 1255-1264. PubMedID: 20802991
- Nguyen KT, Adamkiewicz MA, Hebert LE, Zygiel EM, Boyle HR, Martone CM, Meléndez-Ríos CB, Noren KA, Noren CJ, Hall MF (2014) Identification and characterization of mutant clones with enhanced propagation rates from phage-displayed peptide libraries Anal Biochem; 462C, 35-43. PubMedID: 24952360, DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2014.06.007
- Gonzalez, A.M. et al. (2011) Targeting choroid plexus epithelia and ventricular ependyma for drug delivery to the central nervous system BMC Nurosci; PubMedID: 21214926
- Kim, M. (2011) A peptide to dimerized translationally controlled tumor protein modulates allergic reactions J Mol Med; PubMedID: 21384150
- Guo, C.P. et al. (2011) Potent Anti-Tumor Effect Generated by a Novel Human Papilllomavirus (HPV) Antagonist Peptide Reactivating the pRb/E2F Pathway PLoS One; PubMedID: 21423621
- Kanki, S. et al. (2011) Identification of targeting peptides for ischemic myocardium by in vivo phage display J Mol Cell Cardiol; PubMedID: 21316369
- Mier, W. et al. (2007) Influence of chelate conjugation on a newly identified tumor-targeting peptide J Nucl Med; 48, 1545-1552. PubMedID: 17704241
- Kelly, K.A. et al. (2008) Targeted nanoparticles for imaging incipient pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma PLoS Med; 5, 657-688. PubMedID: 18416599
- Kaur K, Taneja NK, Dhingra S, Tyagi JS (2014) DevR (DosR) mimetic peptides impair transcriptional regulation and survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis under hypoxia by inhibiting the autokinase activity of DevS sensor kinase BMC Microbiol; 14, 195. PubMedID: 25048654, DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-14-195
- Li, Z.J. et. al. (2010) A novel peptide specifically targeting the vasculature of orthotopic colorectal cancer for imaging detection and drug delivery J Control Release; 148, 292-302. PubMedID: 20854857
- Cao, Q. et al. (2010) Phage display probes for imaging early response to bevacizumab treatment Amino Acids; PubMedID: 20232090
- Liu, J. et al. (2010) Novel peptide-dendrimer conjugates as drug carriers for targeting nonsmall cell lung cancer Int J Namomedicine; 6, 59-69. PubMedID: 21289982
- Lu, S. et al. (2010) Targeting of embryonic stem cells by peptide-conjugated quantum dots PLoS One; 5, PubMedID: 20711469
- Larbanoix, L. et al. (2010) Potential amyloid plaque-specific peptides for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease Neurobiol Aging; 31, 1679-1689. PubMedID: 19027991
- Mai, J. et al. (2009) A synthetic peptide mediated actvie targeting of cisplatin liposomes to Tie2 expressing cells J Control Release; 139, 174-181. PubMedID: 19576253
- Epitope mapping
- Identification of protein-protein contacts (1) and enzyme inhibitors (2)
- Discovery of peptide ligands for GroEL (3), HIV (4-7), semiconductor surfaces (8) and small-molecule fluorophores (9) and drugs (10)
- Bioactive receptor ligands have been identified both by panning against purified receptors (11-14) and against intact cells (15-18)
- Peptides which target specific cell types have been isolated by in vitro panning and used for cell-specific gene delivery (19-22)
- Ligands for mold spores (23) and bacterial cells (24) have also been identified using this system, including a peptide that specifically inhibits anthrax toxin, both in vitro and in vivo (25)
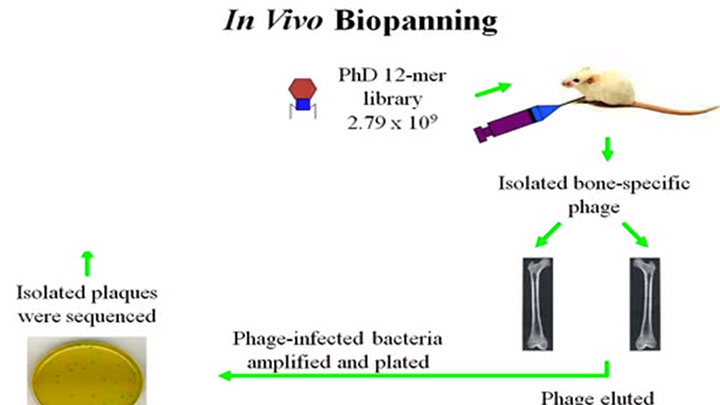
- Tissue-specific peptides have been isolated by in vivo panning, in which phage is injected into a live animal, the relevant organs harvested and phage isolated from each tissue type (26,27)
References
- Berggard, T. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 41954–41959. PMID: 12176979
- Chaudhary, J. et al. (2001) Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 280, C1027–1030. PMID: 11245619
- Chen, L. and Sigler, P.B. (1999) Cell 99, 757–768. PMID: 10619429
- Biorn, A.C. et al. (2004) Biochemistry 43, 1928–1938. PMID: 14967033
- Ferrer, M. and Harrison, S.C. (1999) J. Virol. 73, 5795–5802. PMID: 10364331
- Ferrer, M. et al. (1999) J. Pept. Res. 54, 32–42. PMID: 10448968
- BouHamdan, M. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8009–8016. PMID: 9525900
- Whaley, S.R. et al. (2000) Nature 405, 665–668. PMID: 10864319
- Rozinov, M.N. and Nolan, G.P. (1998) Chem. Biol. 5, 713–728. PMID: 9862799
- Rodi, D.J. et al. (1999) J. Mol. Biol. 285, 197–203. PMID: 9878399
- Kraft, S. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 1979–1985. PMID: 9890954
- Koolpe, M. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 46974–46979. PMID: 12351647
- Mummert, M.E. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Med. 192, 769–779. PMID: 10993908
- Hetian, L. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 43137–43142. PMID: 12183450
- White, S.J. et al. (2001) Hypertension 37, 449–455. PMID: 11230317
- Binetruy-Tournaire, R. et al. (2000) EMBO J. 19, 1525–1533. PMID: 10747021
- Kragler, F. et al. (2000) EMBO J. 19, 2856–2868. PMID: 10856231
- Gazouli, M. et al. (2002) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 303, 627–632. PMID: 12388644
- Romanczuk, H. et al. (1999) Hum. Gene Ther. 10, 2615–2626. PMID: 10566889
- Nicklin, S.A. et al. (2000) Circulation 102, 231–237. PMID: 10889136
- Jost, P.J. et al. (2001) FEBS Lett. 489, 263–269. PMID: 11165262
- Rasmussen, U.B. et al. (2002) Cancer Gene Ther. 9, 606–612. PMID: 12082461
- Tinoco, L.W. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 36351–36356. PMID: 12130641
- Stratmann, J. et al. (2002) J. Clin. Microbiol. 40, 4244–4250. PMID: 12409405
- Mourez, M. et al. (2001) Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 958–961. PMID: 11581662
- Lee, L. et al. (2002) Arthritis Rheum. 46, 2109–2120. PMID: 12209516
- Duerr, D.M. et al. (2004) J. Virol. Methods 116, 177–180. PMID: 14738985
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.