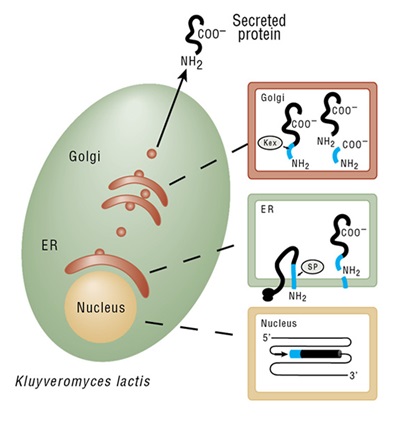
Protein Expression in Yeast
Choose Type:
- Protein expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Cloning a PCR fragment into pKLAC2 (E1000).
- Protein Expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Growth of strains for detection of secreted protein
- Protein Expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Identification of Multi-copy Integrants
- Protein Expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Identification of properly integrated cells
- Protein expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Linearization of pKLAC2 for integrative transformation of K. lactis.
- Protein Expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Simultaneous Expression of Multiple Proteins
- Protein Expression using the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit - Transformation of K. lactis GG799 cells
- Protocol I: Yeast Carbon Base Medium Powder Agar Medium with 5 mM acetamide solution (500 ml)
- Transformation Protocol for K. lactis GG799 Competent Cells (C1001)
-
Avoid Common Obstacles in Protein Expression
Read how to avoid common obstacles in protein expression that prevent interactions with cellular machinery.
-
Why Choose the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit?
Review the advantages of the K. lactis Protein Expression Kit for rapid, high yield protein expression in yeast.
- Protein Expression & Purification Brochure
- Protein Expression and Purification Selection Chart
Feature Articles
Brochures
Selection Tools
- Read, J.D., Colussi, P.A., Ganatra, M.B.and Taron, C.H. (2007) Acetamide Selection of Kluyveromyces lactis Cells Transformed with an Integrative Vector Leads to High Frequency Formation of Multicopy Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol; 73(16), PubMedID: 17586678
- Ganatra, M.B., Rainauskas, S., Hong J.M., Taylor, T.E., Denson, J.P.M., Esposito, D., Read, J.D., Schmeisser, H., Zoon, K.C., Hartley, J.L. and Taron, C.H. (2011) A set of aspartyl protease-deficient strains for improved expression of heterologous proteins in Kluyveromyces lactis FEMS Yeast Res; 11, 168-178. PubMedID: 21166768
- Chuzel, L., Ganatra, M.B., Schermerhorn, K.M., Gardner, A.F., Anton, B.P., Taron, C.H. (2017) Complete genome sequence of Kluyveromyces lactis strain GG799, a common yeast host for heterologous protein expression Genome Announc; 5(30), PubMedID: 28751387
- van Ooyen, A.J.J., Dekker, P., Huang, M., Olsthoorn, M.M.A., Jacobs, D.I., Colussi, P.A.and Taron, C.H. (2006) Heterologous protein production in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. FEMS Yeast Res; 6(3), 381-92. PubMedID: 16630278
- Sakhtah, H., Behler, J., Ali-Reynolds, A., Causey, T.B., Vainauskas, S., Taron, C.H. (2019) A novel regulated hybrid promoter that permits autoinduction of heterologous protein expression in Kluyveromyces lactos Appl Environ Microbiol; pii: e00542-19. PubMedID: 31053583
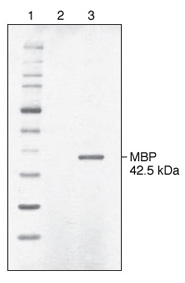
Lane 2: spent culture medium (15 µl) from wild-type K. lactis cells.
Lane 3: spent culture medium (15 µl) from K. lactis cells harboring an integrated expression cassette containing the E. coli malE gene
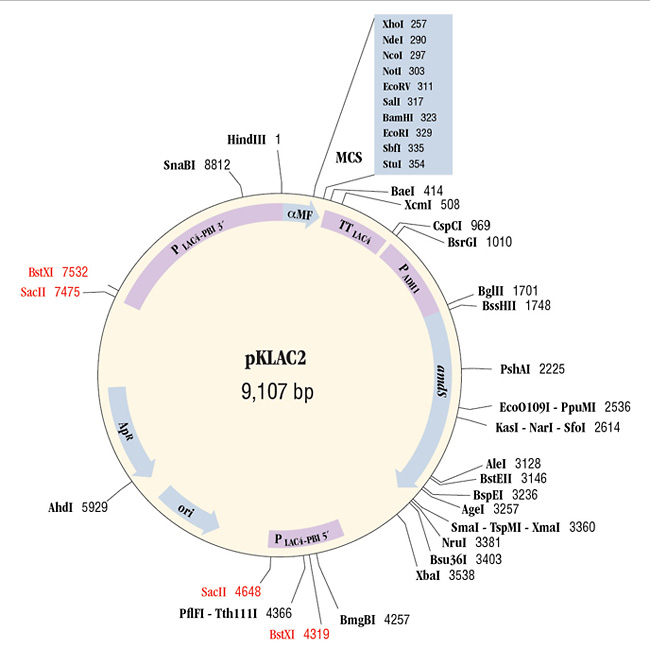
pKLAC2 (9107 bp) contains the 5´ and 3´ ends of the LAC4 promoter (PLAC4-PBI) separated by DNA encoding β-lactamase (ApR) and the pMB1 origin (ori) to allow for its propagation in E. coli. The K. lactis α-mating factor secretion leader sequence (α-MF), multiple cloning site (MCS), and the LAC4 transcription terminator (TT) lie immediately downstream of 3´ PLAC4-PBI. The yeast ADH1 promoter (PADH1) drives expression of an acetamidase selectable marker gene (amdS). The vector can be linearized by digestion with SacII or BstXI to create a linear DNA fragment capable of inserting into the native LAC4 promoter region of the K. lactis genome.
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.