Improvements in Library Quality
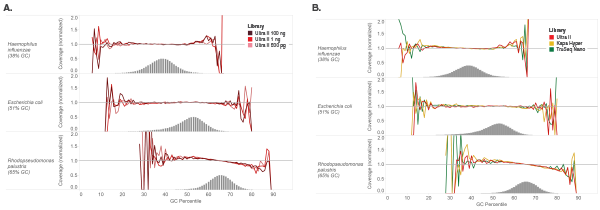
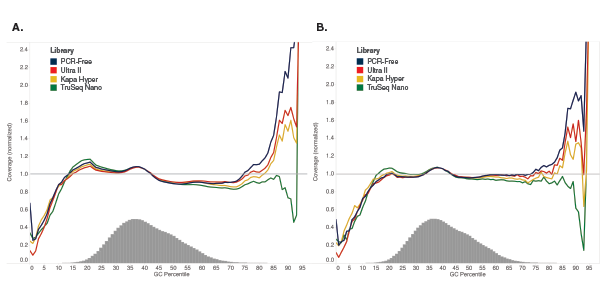
Libraries were made using 100 ng of Human NA19240 genomic DNA and the kits shown, following manufacturers’ recommendations. Libraries were sequenced on an Illumina NextSeq® 500 (A) or MiSeq (B). Reads were mapped to GRCh37 using Bowtie 2.2.4 and GC coverage information was calculated using Picard’s CollectGCBiasMetrics (v1.117). Expected normalized coverage of 1.0 is indicated by the horizontal grey line, the number of 100 bp regions at each GC% is indicated by the vertical grey bars, and the colored lines represent the normalized coverage for each library. Ultra II provides GC coverage most similar to PCR-free libraries and enables coverage across the range of GC content.
| DNA INPUT | LIBRARY KIT | TOTAL READS | % MAPPED | % DUPLICATION | % CHIMERAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 ng | Ultra II | 419,093,838 | 96 | 1.87 | 0.48 |
| Kapa Hyper | 419,097,926 | 96 | 2.00 | 0.60 | |
| TruSeq Nano | 419,086,546 | 97 | 1.91 | 0.53 | |
| 1 ng | Ultra II | 226,860,968 | 96 | 3.96 | 0.44 |
| Kapa Hyper | 226,857,578 | 96 | 11.40 | 0.53 | |
| TruSeq Nano | 226,857,754 | 97 | 34.80 | 0.41 |
Libraries were prepared from Human NA19240 genomic DNA using the input amounts and library prep kits shown, following manufacturers’ recommendations. Libraries were sequenced on the Illumina NextSeq 500. Reads were mapped to the GRCh37 reference using Bowtie 2.2.4. This data illustrates that the NEBNext Ultra II DNA Library Prep Kit enables high quality sequence data, even with very low input amounts.
% Mapped: The percentage of reads mapped to Human GRCh37 reference.
% Duplication: The percentage of mapped sequence that is marked as duplicate.
% Chimeras: The percentage of reads that map outside of a maximum insert size or that have the two ends mapping to different chromosomes.
Coverage of Known Low-Coverage Regions of the Human Genome
Regions of the human genome typically covered at a relatively low level have been identified (2), and the majority of these regions have high GC content. Library preparation can contribute to low and uneven sequence coverage, or even drop-outs, of these challenging regions. Depending on the polymerase used, PCR amplification of a library can result in under-representation of GC-rich regions, and libraries constructed by PCR-free workflows can provide more uniform coverage than amplified libraries (1). Improvements in efficiency and reduction in bias at each step in library preparation, including improved uniformity of library amplification over the full range of GC content improves the evenness of sequence coverage of these regions. Here we show a comparison of sequencing data from human genomic DNA libraries prepared with NEBNext Ultra II and other commercially available kits. Ultra II provided the highest and most uniform coverage of difficult sequence regions, as well as the coverage most similar to the PCR-free library (see below).
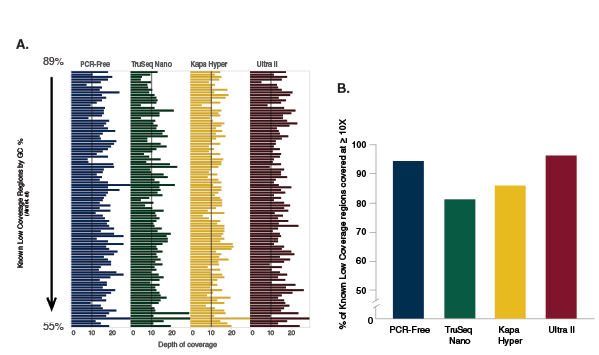
A: Indexed libraries were prepared from 100 ng of Human NA19240 genomic DNA using a PCR-free workflow or the library prep kits shown, following manufacturers’ recommendations. The PCR-free library was prepared using NEBNext Ultra II. Libraries were sequenced on the Illumina NextSeq 500. 420 million reads were randomly extracted from each dataset, to produce an average coverage of 10X. Reads were mapped to the GRCh37 reference genome using Bowtie 2.2.4. Reads on each region were counted using bedtools v2.19.1. The number of reads overlapping distinct difficult, low-coverage regions of the human genome (2) are shown for each library. Ultra II provides the highest and most uniform coverage of these difficult regions, and provides the coverage closest to that obtained with a PCR-free protocol.
B: From the 420 million 75 bp reads randomly extracted from each dataset, 10X coverage was expected. The percentage of difficult regions covered at ≥ 10X is shown for each library prep kit and for the PCR-free workflow. Ultra II provides the highest percentage of reads at ≥ 10X coverage and also provides the coverage closest to that obtained with a PCR-free protocol.
As described above, an ideal library will represent completely and proportionally the sequence of the input DNA. When library preparation is inefficient or when input amounts for a library are very low, there is a risk that the resulting library will lack this diversity, and that some sequences will be over- or under-represented. Comparison of the level of sequence coverage, in 10 kb intervals, achieved with libraries from different input amounts is a useful measure to determine the effect of input amounts on coverage. The increased efficiency of each step in the NEBNext Ultra II library workflow improves the library diversity. Here we show comparisons of libraries prepared for 100 ng, 1 ng and 500 pg human genomic DNA prepared using NEBNext Ultra II. The results demonstrate consistently even coverage for the range of input amounts indicated (see below).
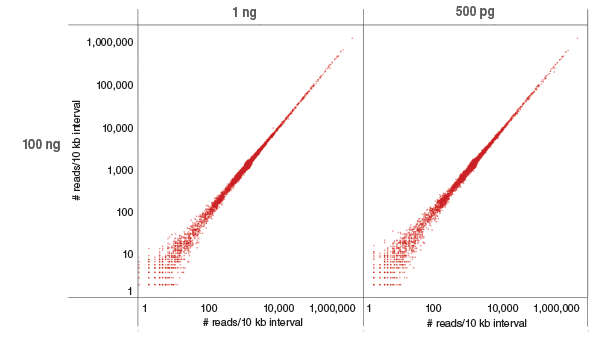
Libraries were prepared with 100 ng, 1 ng and 500 pg of human NA19240 genomic DNA and sequenced on the Illumina NextSeq 500. Each library was downsampled (sambamba view -s) to include 423 M reads and mapped to GRCh37 using Bowtie 2.2.4. Coverage of each 10 kb region of GRCh37 (as determined by bedtools coverage) was compared between low (500 pg and 1 μg) and 100 ng input. Most regions are covered by ~1,000 reads, as expected. Low and high coverage regions are well correlated.
References:
- Kozarewa, I. et al. (2009). Amplification-free Illumina sequencing – library preparation facilitates improved mapping and assembly of (G+C) – biased genomes. Nat. Methods 6:291–295.
- Aird, D. et al. (2011). Analyzing and minimizing PCR amplification bias in Illumina sequencing libraries. Genome Biology 12(2), R18.



