E. coli Expression Strains
Choose Type:
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C2527)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C2528)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C2529)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C2530)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C2566)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C3010)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C3013)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C3026)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C3028)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C3029)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C3030)
- 5 Minute Transformation Protocol (C3037)
- Expression Using SHuffle (C3026)
- Expression Using SHuffle (C3028)
- Expression Using SHuffle (C3029)
- Expression Using SHuffle (C3030)
- High Efficiency Transformation (C2523)
- High Efficiency Transformation Protocol (C2566)
- High Efficiency Transformation Protocol (C3010)
- High Efficiency Transformation Protocol (C3013)
- Transformation Protocol (#C3029, #C3026, #C3028 and #C3030)
- High Efficiency Transformation Protocol (C3037)
- Protein Expression Using BL21(DE3) (C2527)
- Expression Using NEB Express (C2523)
- Protocol for Expression Using NEB Express Iq (C3037)
- Protein Expression Using NiCo21(DE3) (C2529)
- Protocol for Expression Using T7 Express (C2566)
- Protocol for Expression Using T7 Express lysY (C3010)
- Protocol for Expression Using T7 Express Crystal (C3022)
- Protocol for Expression Using T7 Express lysY/Iq (C3013)
- Protocol for Protein Expression Using BL21 (C2530)
- Protocol for Removal of IMAC Contaminating Proteins (C2529)
- Recommended media and expression conditions for T7 Express Crystal (C3022)
- Seleno-methionine Incorporation (C3022)
- Transformation Protocol (C2528)
- Transformation Protocol (C2530)
- Transformation Protocol for BL21(DE3) Competent Cells (C2527)
- High Efficiency Transformation Protocol (C2529)
- Protein Expression with T7 Express strains
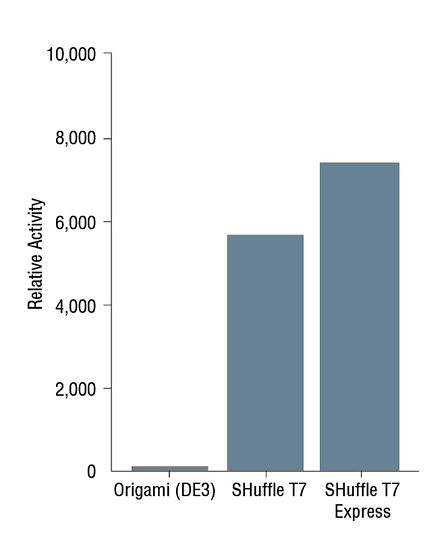
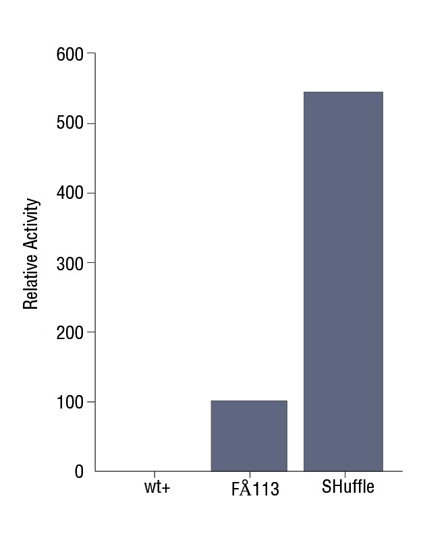
- Expression Using SHuffle®
- Protein Expression Using Lemo21(DE3) (C2528)
- 5 Minute Transformation (C2523)
-
Avoid Common Obstacles in Protein Expression
Read how to avoid common obstacles in protein expression that prevent interactions with cellular machinery.
- Competent Cell Brochure
- Protein Expression & Purification Brochure
- Characteristics of Select E.coli Strains
- Competent Cell Product Comparison
- Competent Cell Selection Guide
- Troubleshooting Transformation Reactions
- Additional E. coli Strain Genotypes
- Electroporation Tips
- Genetic Markers
- Making Unmethylated (Dam- Dcm-) DNA
- McrA, McrBC and EcoKI Strain Phenotypes
- Restriction of Foreign DNA by E. coli K-12
Feature Articles
Brochures
Selection Tools
Troubleshooting Guides
Usage Guidelines
- Schlegel, S., Klepsch, M., Gialama, D., Wickström, D., Slotboom, D.J. and de Gier, J. (2010) Revolutionizing membrane protein overexpression in bacteria Microb Biotechnol; 3 , 403-411 .
- Narayanan, A., Ridilla, M. and Yernool, D.A. (2010) Restrained expression, a method to overproduce toxic membrane proteins by exploiting operator–repressor interactions Protein Sci; 20 , 51-61 .
- Reddy, P.T., Brinson, R.G., Hoopes, J.T., McClung, C., Ke, N., Kashi, L. (2018) Platform development for expression and purification of stable isotope labeled monoclonal antibodies in Escherichia coli. mAbs MAbs; 10 (7), 992-1002. PubMedID: 30060704, DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2018.1496879
- Hibender, S. Landeta, C., Berkmen, M., Beckwith, J., Boyd, D. (2017) Aeropyrum pernix membrane protein VKOR promotes protein disulfide bond formation in two subcellular compartments. Microbiology; 163 (12), 1864-1869. PubMedID: 291309344
- Ren, G., Ke, N. and Berkmen, M. (2016) Use of the Shuffle Strains in Production of Proteins. Curr Protoc Protein Sci; Aug 1, 1;85:5.26.1-5.26.21.. PubMedID: 27479507 , DOI: 10.1002/cpps.11.
- Reuter, W.H., Masuch, T., Ke, N., Lenon, M., Radzinski, M., Van Loi, V., Ren, G., Riggs, P., Antelmann, H., Reichmann, D., Leichert, L.I., Berkmen, M (2019) Utilizing redox-sensitive GFP fusions to detect in vivo redox changes in a genetically engineered prokaryote Redox Biol; 26, 101280. PubMedID: 31450103, DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101280
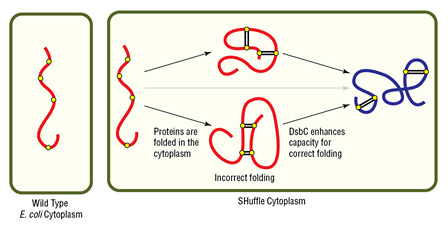
- Oxidizing cytoplasmic environment enables disulfide bond formation
- DsbC (disulfide bond isomerase) directs correct disulfide bond formation
- DsbC also acts as a general chaperone for protein folding
- Cytoplasmic expression increases protein yield
- A wide range of antibiotics can be used for plasmid maintenance (Amp, Kan, Tet, Cam [except for lysY versions])
- Transformation efficiency: 1 x 106 cfu/µg pUC19 DNA
- Protease deficient
- TI phage resistant (fhuA2)
- Free of animal products
- Free of animal products
- T1 phage resistance (fhuA2)
- Media and control plasmid included with most strains
- A variety of convenient formats, including single use transformation tubes and, on request, 96 well plates
- Bulk sales capabilities with custom packaging
Origami™ is a trademark of Invitrogen.
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.