Challenges and Relevance of Glycobiology
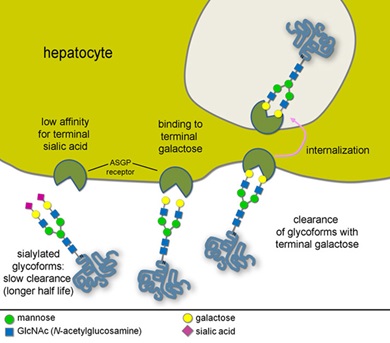
Return to Glycobiology & ProteomicsGlycosylation is not coded by a template and therefore cannot be predicted from the genome. Furthermore, unlike proteins or DNA, glycans often do not have a linear structure. Monosaccharide components can have greatly different biological properties while having the same molecular composition and are therefore indistinguishable by most analytical methods. Glycan heterogeneity adds another level of complexity; a range of glycan variations can be found in the same protein giving rise to a group of related, but not identical, proteins (or glycoforms). The inherent complexity of glycosylation makes it necessary to employ orthogonal analytical techniques to elucidate the structure of each glycoconjugate and to understand its biological function(s).
- Carbohydrates can significantly affect protein structure and therefore influence protein function.
- Many recombinant biopharmaceutical products on the market are glycoproteins; often the quality and safety of these products is influenced by the carbohydrate moieties.
- Recombinant monoclonal antibodies (rMABs), which have a conserved glycosylation site in the Fc domain of the molecule, are increasingly developed as biotherapeutics to treat rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases.
- Recent progress in chemical synthesis and bioengineering has resulted in the development of many carbohydrate-based vaccines, some of which have applications in cancer treatment.
- Heparin, one of the oldest drug agents to date, is a proteoglycan that is still widely used to treat a broad range of conditions.