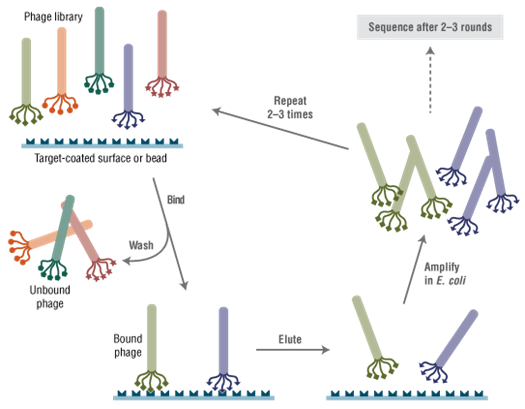
Phage Display
Choose Type:
- Cross-linking of IgG to Protein A or G Beads
- Immunoprecipitation using Protein A/G Magnetic Beads
- Isolation of MBP-fusion protein using Amylose Magnetic Beads
- M13 Amplifcation Protocol for Ph.D. Phage Display
- Phage Display: Solution-phase Panning with Affinity Bead Capture
- mRNA Isolation using Streptavidin Magnetic Beads (NEB #S1420 and NEB #S1421)
- Purification of IgG using Protein A/G Magnetic Beads
- Use of M13KO7 Helper Phage for isolation of single-stranded phagemid DNA
- Protocol for Cloning Peptide Display Libraries in M13KE
- M13 Titer Protocol for Ph.D. Phage Display
- Western Blot (NEB #E8033)
-
Applications of the Ph.D. Phage Display Peptide Libraries
Feature Articles
- Matochko WL, Cory Li S, Tang SK, Derda R (2014) Prospective identification of parasitic sequences in phage display screens Nucleic Acids Res; 42(3), 1784-98. PubMedID: 24217917, DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt1104
- Shires K, Shankland I, Mowla S, Njikan S, Jaymacker J, Novitzky N (2014) Serine and proline-rich ligands enriched via phage-display technology show preferential binding to BCR/ABL expressing cells Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther; 7(1), 32-40. PubMedID: 24480037, DOI: 10.1016/j.hemonc.2014.01.001
- Baumgartner J, Carillo MA, Eckes KM, Werner P, Faivre D. (2014) Biomimetic Magnetite Formation From Biocombinatorial Approaches to Mineralization Effects Langmuir; 30(8), 2129-36. PubMedID: 24499323, DOI: 10.1021/la404290c
- Nguyen KT, Adamkiewicz MA, Hebert LE, Zygiel EM, Boyle HR, Martone CM, Meléndez-Ríos CB, Noren KA, Noren CJ, Hall MF (2014) Identification and characterization of mutant clones with enhanced propagation rates from phage-displayed peptide libraries Anal Biochem; 462C, 35-43. PubMedID: 24952360, DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2014.06.007
- Fatima A, Wang H, Kang K, Xia L, Wang Y, Ye W, Wang J, Wang X. (2014) Development of VHH Antibodies against Dengue Virus Type 2 NS1 and Comparison with Monoclonal Antibodies for Use in Immunological Diagnosis PLoS One; 9(4), e95263. PubMedID: 24751715, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095263
- McGuire MJ, Gray BP, Li S, Cupka D, Byers LA, Wu L, Rezaie S, Liu YH, Pattisapu N, Issac J, Oyama T, Diao L, Heymach JV, Xie XJ, Minna JD, Brown KC (2014) Identification and Characterization of a Suite of Tumor Targeting Peptides for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Sci Rep; 4, 4480. PubMedID: 24670678, DOI: 10.1038/srep04480
- Kaur K, Taneja NK, Dhingra S, Tyagi JS (2014) DevR (DosR) mimetic peptides impair transcriptional regulation and survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis under hypoxia by inhibiting the autokinase activity of DevS sensor kinase BMC Microbiol; 14, 195. PubMedID: 25048654, DOI: 10.1186/1471-2180-14-195
- Grin I, Hartmann MD, Sauer G, Hernandez Alvarez B, Schütz M, Wagner S, Madlung J, Macek B, Felipe-Lopez A, Hensel M, Lupas A, Linke D (2014) A trimeric lipoprotein assists in trimeric autotransporter biogenesis in enterobacteria J Biol Chem; 289(11), 7388-98. PubMedID: 24369174, DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.513275
- Maneewatch S, Adisakwattana P, Chaisri U, Saengjaruk P, Srimanote P, Thanongsaksrikul J, Sakolvaree Y, Poungpan P, Chaicumpa W (2014) Therapeutic epitopes of Leptospira LipL32 protein and their characteristics Protein Eng Des Sel; 27(5), 135-44. PubMedID: 24760832, DOI: 10.1093/protein/gzu006
- Cieslewicz, M. et al (2013) Targeted delivery of proapoptotic peptides to tumor-associated macrophages improves survival Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A; 110, 15919-24. PubMedID: 24046373, DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1312197110
- Lu, R.-M. et al (2013) Targeted drug delivery systems mediated by a novel peptide in breast cancer therapy and imaging PLoS One; 8(6), e66128. PubMedID: 23776619, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0066128
- Gonzalez, A.M. et al. (2011) Targeting choroid plexus epithelia and ventricular ependyma for drug delivery to the central nervous system BMC Nurosci; PubMedID: 21214926
- Balian, G. et al. (2010) Peptides from phage display library modulate gene expression in mesenchymal cells and potentiate osteogenesis in unicortical bone defects J Vis Exp; 46, PubMedID: 21178970
- Cao, Q. et al. (2010) Phage display probes for imaging early response to bevacizumab treatment Amino Acids; PubMedID: 20232090
- Wu, C. and Tzertzinis, G.
- Epitope mapping
- Identification of protein-protein contacts (1) and enzyme inhibitors (2)
- Discovery of peptide ligands for GroEL (3), HIV (4-7), semiconductor surfaces (8) and small-molecule fluorophores (9) and drugs (10)
- Bioactive receptor ligands have been identified both by panning against purified receptors (11-14) and against intact cells (15-18)
- Peptides which target specific cell types have been isolated by in vitro panning and used for cell-specific gene delivery (19-22)
- Ligands for mold spores (23) and bacterial cells (24) have also been identified using this system, including a peptide that specifically inhibits anthrax toxin, both in vitro and in vivo (25)
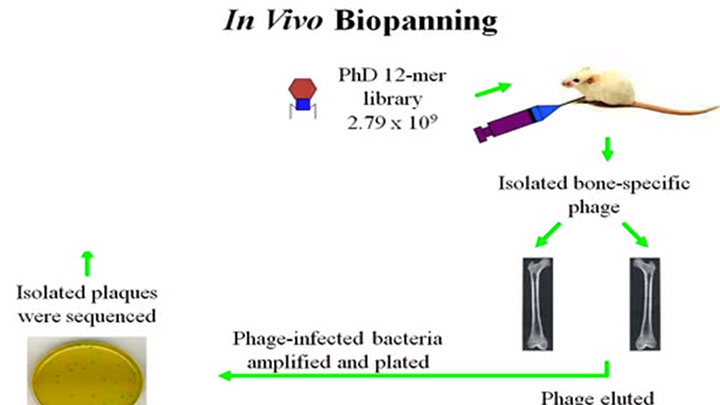
- Tissue-specific peptides have been isolated by in vivo panning, in which phage is injected into a live animal, the relevant organs harvested and phage isolated from each tissue type (26,27)
References
- Berggard, T. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 41954–41959. PMID: 12176979
- Chaudhary, J. et al. (2001) Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 280, C1027–1030. PMID: 11245619
- Chen, L. and Sigler, P.B. (1999) Cell 99, 757–768. PMID: 10619429
- Biorn, A.C. et al. (2004) Biochemistry 43, 1928–1938. PMID: 14967033
- Ferrer, M. and Harrison, S.C. (1999) Ji. Virol. 73, 5795–5802. PMID: 10364331
- Ferrer, M. et al. (1999) J. Pept. Res. 54, 32–42. PMID: 10448968
- BouHamdan, M. et al. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8009–8016. PMID: 9525900
- Whaley, S.R. et al. (2000) Nature 405, 665–668. PMID: 10864319
- Rozinov, M.N. and Nolan, G.P. (1998) Chem. Biol. 5, 713–728. PMID: 9862799
- Rodi, D.J. et al. (1999) J. Mol. Biol. 285, 197–203. PMID: 9878399
- Kraft, S. et al. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 1979–1985. PMID: 9890954
- Koolpe, M. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 46974–46979. PMID: 12351647
- Mummert, M.E. et al. (2000) J. Exp. Med. 192, 769–779. PMID: 10993908
- Hetian, L. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 43137–43142. PMID: 12183450
- White, S.J. et al. (2001) Hypertension 37, 449–455. PMID: 11230317
- Binetruy-Tournaire, R. et al. (2000) EMBO J. 19, 1525–1533. PMID: 10747021
- Kragler, F. et al. (2000) EMBO J. 19, 2856–2868. PMID: 10856231
- Gazouli, M. et al. (2002) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 303, 627–632. PMID: 12388644
- Romanczuk, H. et al. (1999) Hum. Gene Ther. 10, 2615–2626. PMID: 10566889
- Nicklin, S.A. et al. (2000) Circulation 102, 231–237. PMID: 10889136
- Jost, P.J. et al. (2001) FEBS Lett. 489, 263–269. PMID: 11165262
- Rasmussen, U.B. et al. (2002) Cancer Gene Ther. 9, 606–612. PMID: 12082461
- Tinoco, L.W. et al. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 36351–36356. PMID: 12130641
- Stratmann, J. et al. (2002) J. Clin. Microbiol. 40, 4244–4250. PMID: 12409405
- Mourez, M. et al. (2001) Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 958–961. PMID: 11581662
- Lee, L. et al. (2002) Arthritis Rheum. 46, 2109–2120. PMID: 12209516
- Duerr, D.M. et al. (2004) J. Virol. Methods 116, 177–180. PMID: 14738985
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.