Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases
Fidelity at its finest – for over 10 years.
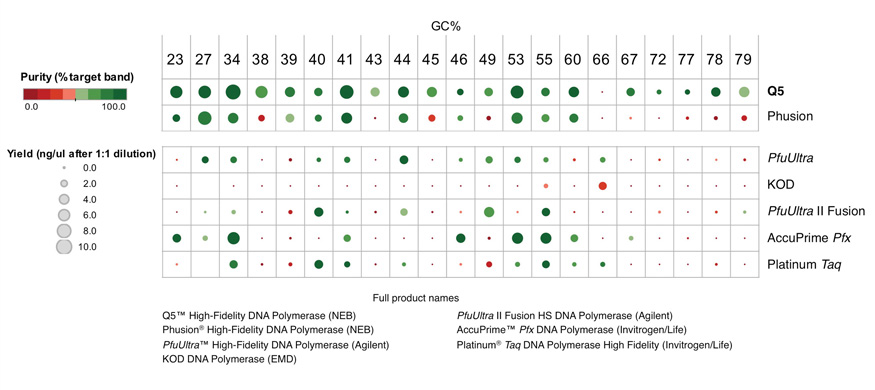
Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (NEB #M0491) sets a new standard for both fidelity and robust performance. With fidelity >280 times higher than Taq, Q5 results in ultra-low error rates. Q5 is a novel polymerase that is fused to the processivity-enhancing Sso7d DNA binding domain, improving speed, fidelity and reliability of performance.
Q5 is also available in a hot start format (NEB #M0493). In contrast to chemically modified or antibody-based hot start polymerases, Q5 Hot Start High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase utilizes engineered oligonucleotides known as aptamers. The aptamer binds to the polymerase through non-covalent interactions, blocking enzyme activity during the reaction setup, and is dissociated during normal cycling conditions. Reactions can be set up at room temperature and a separate high temperature activation step is not required, shortening reaction times.
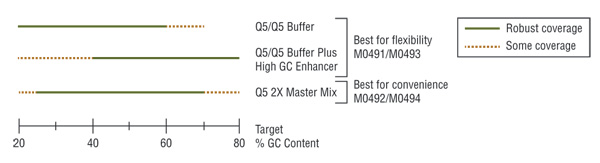
Q5 master mixes (NEB #M0492, #M0494) contain dNTPs, Mg++ and a proprietary broad-use buffer requiring only the addition of primers and DNA template for robust amplification, regardless of GC content.
Q5U® Hot Start High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (NEB #M0515) is a modified version of Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase containing a mutation in the uracil-binding pocket that enables the ability to read and amplify templates containing uracil and inosine bases. This is useful for amplifying bisulfite-converted, enzymatically-deaminated, or damaged DNA, preventing carryover contamination in PCR (when used with dUTP and UDG), and in USER cloning methods. Learn more about this product.
The LunaScript® Multiplex One-Step RT-PCR Kit (NEB #E1555) combines Q5 with the thermostable Luna® WarmStart® Reverse Transcriptase for a streamlined one-step RT-PCR protocol with superior multiplexing and sensitivity down to 0.01 pg of human total RNA. Learn more about this product.
NEW: Q5 Blood Direct 2X Master Mix (NEB #M0500) can amplify a wide variety of targets direct from dried blood spots or up to 30% whole human blood, skipping DNA purification. Learn more about this product.
Choose Type:
- PCR Using NEBNext® High-Fidelity 2X PCR Master Mix (M0541)
- PCR Using Q5® Hot Start High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (M0493)
- Protocol for Q5® Hot Start High-Fidelity 2X Master Mix
- Protocol for Q5® High-Fidelity 2X Master Mix
- PCR Optimization (E0555)
- Protocol for a Routine PCR (E0555)
- PCR Using Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (M0491)
- Protocol for a PCR reaction using NEBNext® Q5® Hot Start HiFi PCR Master Mix (M0543)
- Protocol for a PCR reaction using NEBNext® Ultra™ II Q5® Master Mix (M0544)
-
Polymerase Fidelity: What is it, and what does it mean for your PCR?
-
Using aptamers to control enzyme activity: Hot Start Taq and beyond
This article describes the use of engineered oligonucleotides known as aptamers in regulating the enzyme activity of polymerases and reverse transcriptases.
-
Understanding Variability in DNA Amplification Reactions
-
Anatomy of a Polymerase - How Function and Structure are Related
Read about the relationship between Polymerase structure and function when copying DNA.
- PCR Reagents Brochure
- DNA Polymerase Selection Chart
- PCR Troubleshooting Guide
- Guidelines for PCR Optimization with Thermophilic DNA Polymerases
Feature Articles
Brochures
Selection Tools
Troubleshooting Guides
Usage Guidelines
- Amin Zargar, David N Quan, Milad Emamian, Chen Yu Tsao, Hsuan-Chen Wu, Chelsea R Virgile, William E Bentley (2015) Rational design of 'controller cells' to manipulate protein and phenotype expression. Metab Eng; PubMedID: 25908186, DOI: 10.1016/j.ymben.2015.04.001
- Yuan Xue, Jossef Osborn, Anand Panchal, Jay L Mellies (2015) The RpoE Stress Response Pathway Mediates Reduction of the Virulence of Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by Zinc. Appl Environ Microbiol; 81, 3766-74. PubMedID: 25819956, DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00507-15
- Longhai Dai, Can Liu, Yueming Zhu, Jiangsheng Zhang, Yan Men, Zeng Yan, Yuanxia Sun (2015) Functional Characterization of Cucurbitadienol Synthase and Triterpene Glycosyltransferase Involved in Biosynthesis of Mogrosides from Siraitia grosvenorii. Plant Cell Physiol; PubMedID: 25759326, DOI: 10.1093/pcp/pcv043
- Jun Wu, Daiji Okamura, Mo Li, Keiichiro Suzuki, Chongyuan Luo, Li Ma, Yupeng He, Zhongwei Li, Chris Benner, Isao Tamura, Marie N Krause, Joseph R Nery, Tingting Du, Zhuzhu Zhang, Tomoaki Hishida, Yuta Takahashi, Emi Aizawa, Na Young Kim, Jeronimo Lajara, Pedro Guillen, Josep M Campistol, Concepcion Rodriguez Esteban, Pablo J Ross, Alan Saghatelian, Bing Ren, Joseph R Ecker, Juan Carlos Izpisua Belmonte (2015) An alternative pluripotent state confers interspecies chimaeric competency. Nature; PubMedID: 25945737, DOI: 10.1038/nature14413
- Harish Nag Kankipati, Marta Rubio-Texeira, Dries Castermans, George Diallinas, Johan M Thevelein (2015) Sul1 and Sul2 Sulfate Transceptors Signal to Protein Kinase A upon Exit of Sulfur Starvation. J Biol Chem; 290, 10430-46. PubMedID: 25724649, DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.629022
- Yonghe Zhang, Huiming Huang, Shanshan Xu, Bo Wang, Jianhua Ju, Huarong Tan, Wenli Li (2015) Activation and enhancement of Fredericamycin A production in deepsea-derived Streptomyces somaliensis SCSIO ZH66 by using ribosome engineering and response surface methodology. Microb Cell Fact; 14, 64. PubMedID: 25927229, DOI: 10.1186/s12934-015-0244-2
- Yafeng Li, Delu Song, Ying Song, Liangliang Zhao, Natalie Wolkow, John W Tobias, Wenchao Song, Joshua L Dunaief (2015) Iron-induced Local Complement Component 3 (C3) Up-regulation via Non-canonical Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)-β Signaling in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium. J Biol Chem; 290, 11918-34. PubMedID: 25802332, DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.645903
- Christine Henke, Pamela L Strissel, Maria-Theresa Schubert, Megan Mitchell, Claus C Stolt, Florian Faschingbauer, Matthias W Beckmann, Reiner Strick (2015) Selective expression of sense and antisense transcripts of the sushi-ichi-related retrotransposon - derived family during mouse placentogenesis. Retrovirology; 12, 9. PubMedID: 25888968, DOI: 10.1186/s12977-015-0138-8
- Binyamin D Berkovits, Christine Mayr (2015) Alternative 3' UTRs act as scaffolds to regulate membrane protein localization. Nature; PubMedID: 25896326, DOI: 10.1038/nature14321
- Vladimir Potapov, Jennifer L. Ong. (2017) Examining Sources of Error in PCR by Single-Molecule Sequencing. PLOS One; PubMedID: 28683110
- Martin Kostovcik, Craig C Bateman, Miroslav Kolarik, Lukasz L Stelinski, Bjarte H Jordal, Jiri Hulcr (2014) The ambrosia symbiosis is specific in some species and promiscuous in others: evidence from community pyrosequencing. ISME J; PubMedID: 25083930, DOI: 10.1038/ismej.2014.115
- Bert De Rybel, Milad Adibi, Alice S. Breda, Jos R. Wendrich, Margot E. Smit, Ondej Novk, Nobutoshi Yamaguchi, Saiko Yoshida, Gert Van Isterdael, Joakim Palovaara, Bart Nijsse, Mark V. Boekschoten, Guido Hooiveld, Tom Beeckman, Doris Wagner, Karin Ljung, Christian Fleck, Dolf Weijers (2014) Integration of growth and patterning during vascular tissue formation in Arabidopsis Science; 345, 1255215. PubMedID: 25104393, DOI: 10.1126/science.1255215
- Vidhyadhar Nandana, Sushant Singh, Abhay Narayan Singh, Vikash Kumar Dubey (2014) Procerain B, a cysteine protease from Calotropis procera, requires N-terminus pro-region for activity: cDNA cloning and expression with pro-sequence. Protein Expr Purif; 103C, 16-22. PubMedID: 25173974, DOI: 10.1016/j.pep.2014.08.003
- Xin Duan, Arjun Krishnaswamy, Irina De la Huerta, Joshua R Sanes (2014) Type II Cadherins Guide Assembly of a Direction-Selective Retinal Circuit. Cell; 158, 793-807. PubMedID: 25126785, DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.047
- Connelly CM1, Porter LR2, TerMaat JR (2014) PCR amplification of a triple-repeat genetic target directly from whole blood in 15 minutes as a proof-of-principle PCR study for direct sample analysis for a clinically relevant target BMC Med Genet; 15, 130. PubMedID: 25495904, DOI: 10.1186/s12881-014-0130-5
Products and content are covered by one or more patents, trademarks and/or copyrights owned or controlled by New England Biolabs, Inc (NEB). The use of trademark symbols does not necessarily indicate that the name is trademarked in the country where it is being read; it indicates where the content was originally developed. The use of this product may require the buyer to obtain additional third-party intellectual property rights for certain applications. For more information, please email busdev@neb.com.
This product is intended for research purposes only. This product is not intended to be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes in humans or animals.